Cytotoxicity and DNA cleavage with core-shell nanocomposites functionalized by a KH domain DNA binding peptide
- PMID: 23824281
- PMCID: PMC3825787
- DOI: 10.1039/c3nr02203j
Cytotoxicity and DNA cleavage with core-shell nanocomposites functionalized by a KH domain DNA binding peptide
Abstract
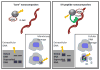
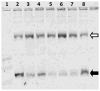
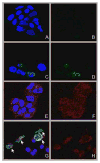
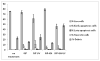
A nanoconjugate was composed of metal oxide nanoparticles decorated with peptides and fluorescent dye and tested for DNA cleavage following UV light activation. The peptide design was based on a DNA binding domain, the so called KH domain of the hnRNPK protein. This "KH peptide" enabled cellular uptake of nanoconjugates and their entry into cell nuclei. The control nanoconjugate carried no peptide; it consisted only of the metal oxide nanoparticle prepared as Fe3O4@TiO2 nanocomposite and the fluorescent dye alizarin red S. These components of either construct are responsible for nanoconjugate activation by UV light and the resultant production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Production of ROS at different subcellular locations causes damage to different components of cells: only nanoconjugates inside cell nuclei can be expected to cause DNA cleavage. Degradation of cellular DNA with KH peptide decorated nanoconjugates exceeded the DNA damage obtained from control, no-peptide nanoconjugate counterparts. Moreover, caspase activation and cell death were more extensive in the same cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of Fe3O4 core-TiO2 shell nanocomposites and nanoconjugates as a foundation for neuroblastoma radiosensitization.Cancer Nanotechnol. 2021;12(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12645-021-00081-z. Epub 2021 May 14. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34777621 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional Fe3O4-TiO2 nanocomposites for magnetic resonance imaging and potential photodynamic therapy.Nanoscale. 2013 Mar 7;5(5):2107-13. doi: 10.1039/c3nr33978e. Epub 2013 Feb 5. Nanoscale. 2013. PMID: 23381832
-
Copper(II) oxide nanoparticles augment antifilarial activity of Albendazole: In vitro synergistic apoptotic impact against filarial parasite Setaria cervi.Int J Pharm. 2016 Mar 30;501(1-2):49-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.01.059. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Int J Pharm. 2016. PMID: 26827921
-
Synthesis, characterisation, cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of functionalised magnetic ruthenium (II) polypyridine complex core-shell nanocomposite.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018 Jan;178:270-276. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2017.10.037. Epub 2017 Nov 3. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2018. PMID: 29172134
-
Zinc oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, antiseptic activity and toxicity mechanism.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017 Nov;249:37-52. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2017.07.033. Epub 2017 Aug 26. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017. PMID: 28923702 Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular in situ labeling of TiO2 nanoparticles for fluorescence microscopy detection.Nano Res. 2018 Jan;11(1):464-476. doi: 10.1007/s12274-017-1654-8. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Nano Res. 2018. PMID: 29541425 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of Iron Oxide Core-Titanium Dioxide Shell Nanoparticles in VX2 Tumor Bearing Rabbits Introduced by Two Different Delivery Modalities.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2016 Aug 3;6(8):143. doi: 10.3390/nano6080143. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28335271 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor targeted nuclear delivery and high-resolution whole cell X-ray imaging of Fe3O4@TiO2 nanoparticles in cancer cells.ACS Nano. 2013 Dec 23;7(12):10502-17. doi: 10.1021/nn4033294. Epub 2013 Nov 27. ACS Nano. 2013. PMID: 24219664 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Fe3O4 core-TiO2 shell nanocomposites and nanoconjugates as a foundation for neuroblastoma radiosensitization.Cancer Nanotechnol. 2021;12(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12645-021-00081-z. Epub 2021 May 14. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34777621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailar JC, 3rd, Gornik HL. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1569–1574. - PubMed
-
- Greish K. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;624:25–37. - PubMed
-
- LaRocque J, Bharali DJ, Mousa SA. Mol Biotechnol. 2009;42:358–366. - PubMed
-
- Talekar M, Kendall J, Denny W, Garg S. Anticancer Drugs. 2011;22:949–962. - PubMed
-
- Wamer WG, Yin JJ, Wei RR. Free Radic Biol Med. 1997;23:851–858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

