Clinical pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and drug-interaction profile of the integrase inhibitor dolutegravir
- PMID: 23824675
- PMCID: PMC3805712
- DOI: 10.1007/s40262-013-0093-2
Clinical pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and drug-interaction profile of the integrase inhibitor dolutegravir
Abstract
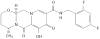
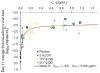
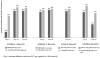
Dolutegravir is a second-generation integrase strand transfer inhibitor (INSTI) currently under review by the US Food and Drug Administration for marketing approval. The in vitro, protein-adjusted 90 % inhibitory concentration (IC90) of dolutegravir for wild-type virus is 0.064 μg/ml, and it retains in vitro anti-HIV 1 activity across a broad range of viral phenotypes that are known to confer resistance to the currently marketed INSTIs, raltegravir and elvitegravir. Dolutegravir has a terminal elimination half-life of 13-14 h and maintains concentrations over the in vitro, protein-adjusted IC90 for more than 30 h following a single dose. Additionally, dolutegravir has low inter-subject variability compared with raltegravir and elvitegravir. A plasma exposure-response relationship has been well described, with antiviral activity strongly correlating with trough concentrations. Phase III trials have assessed the antiviral activity of dolutegravir compared with efavirenz and raltegravir in antiretroviral (ARV)-naive patients and found that dolutegravir achieved more rapid and sustained virologic suppression in both instances. Additionally, studies of dolutegravir activity in patients with known INSTI-resistant mutations have been favourable, indicating that dolutegravir retains activity in a variety of INSTI-resistant phenotypes. Much like currently marketed INSTIs, dolutegravir is very well tolerated. Because dolutegravir inhibits the renal transporter organic cation transporter 2, reduced tubular secretion of creatinine leads to non-progressive increases in serum creatinine. These serum creatinine increases have not been associated with a decreased glomerular filtration rate or progressive renal impairment. Dolutegravir's major and minor metabolic pathways are uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 and cytochrome P450 (CYP)-3A4, respectively, and it neither induces nor inhibits CYP isoenzymes. Thus dolutegravir has a modest drug interaction profile. However, antacids significantly decrease dolutegravir plasma exposure and should be separated by 2 h before, or 6 h after, a dolutegravir dose. In summary, dolutegravir is the first of the second-generation INSTIs and exhibits a predictable pharmacokinetic profile and a well-defined exposure-response relationship. Dolutegravir retains activity despite the presence of some class-resistant mutations and achieves rapid and sustained virologic suppression in ARV-naive and ARV-experienced patients. Clinically, dolutegravir is poised to become a commonly used component of antiretroviral regimens.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Dejesus E, Cohen C, Elion R, et al. First report of raltegravir (RAL, MK-0518) use after virologic rebound on elvitegravir (EVT, GS 9137) [abstract no. TUPEB032 plus poster]. 4th IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention; 2007 Jul 22–25; Sydney.
-
- Hazuda DJ, Miller MD, Nguyen BY, et al. Resistance to the HIV-integrase inhibitor raltegravir: analysis of protocol 005, a phase 2 study in patients with triple-class resistant HIV-1 infection [abstract no. 8]. 16th International HIV Drug Resistance Workshop; 2007 Jun 12–16; Barbados.
-
- McColl DJ, Fransen S, Gupta S, et al. Resistance and cross-resistance to first generation integrase inhibitors: Insights from a phase 2 study of Elvitegravir (GS-9137). [abstract no. 9]. 16th International HIV Drug Resistance Workshop; 2007 Jun 12–16; Barbados.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

