Ebolavirus VP35 coats the backbone of double-stranded RNA for interferon antagonism
- PMID: 23824825
- PMCID: PMC3753998
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01452-13
Ebolavirus VP35 coats the backbone of double-stranded RNA for interferon antagonism
Abstract
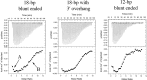
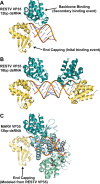
Recognition of viral double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) activates interferon production and immune signaling in host cells. Crystal structures of ebolavirus VP35 show that it caps dsRNA ends to prevent sensing by pattern recognition receptors such as RIG-I. In contrast, structures of marburgvirus VP35 show that it primarily coats the dsRNA backbone. Here, we demonstrate that ebolavirus VP35 also coats the dsRNA backbone in solution, although binding to the dsRNA ends probably constitutes the initial binding event.
Figures
References
-
- Bale S, Julien JP, Bornholdt ZA, Kimberlin CR, Halfmann P, Zandonatti MA, Kunert J, Kroon GJ, Kawaoka Y, Macrae IJ, Wilson IA, Saphire EO. 2012. Marburg virus VP35 can both fully coat the backbone and cap the ends of dsRNA for interferon antagonism. PLoS Pathog. 8:e1002916.10.1371/journal.ppat.1002916 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chao JA, Lee JH, Chapados BR, Debler EW, Schneemann A, Williamson JR. 2005. Dual modes of RNA-silencing suppression by Flock House virus protein B2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 12:952–957 - PubMed
-
- Cheng A, Wong SM, Yuan YA. 2009. Structural basis for dsRNA recognition by NS1 protein of influenza A virus. Cell Res. 19:187–195 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

