Working memory impairment in calcineurin knock-out mice is associated with alterations in synaptic vesicle cycling and disruption of high-frequency synaptic and network activity in prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 23825400
- PMCID: PMC3718364
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5362-12.2013
Working memory impairment in calcineurin knock-out mice is associated with alterations in synaptic vesicle cycling and disruption of high-frequency synaptic and network activity in prefrontal cortex
Abstract
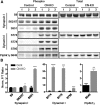
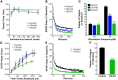
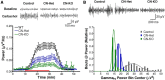
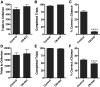
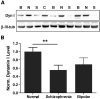
Working memory is an essential component of higher cognitive function, and its impairment is a core symptom of multiple CNS disorders, including schizophrenia. Neuronal mechanisms supporting working memory under normal conditions have been described and include persistent, high-frequency activity of prefrontal cortical neurons. However, little is known about the molecular and cellular basis of working memory dysfunction in the context of neuropsychiatric disorders. To elucidate synaptic and neuronal mechanisms of working memory dysfunction, we have performed a comprehensive analysis of a mouse model of schizophrenia, the forebrain-specific calcineurin knock-out mouse. Biochemical analyses of cortical tissue from these mice revealed a pronounced hyperphosphorylation of synaptic vesicle cycling proteins known to be necessary for high-frequency synaptic transmission. Examination of the synaptic vesicle cycle in calcineurin-deficient neurons demonstrated an impairment of vesicle release enhancement during periods of intense stimulation. Moreover, brain slice and in vivo electrophysiological analyses showed that loss of calcineurin leads to a gene dose-dependent disruption of high-frequency synaptic transmission and network activity in the PFC, correlating with selective working memory impairment. Finally, we showed that levels of dynamin I, a key presynaptic protein and calcineurin substrate, are significantly reduced in prefrontal cortical samples from schizophrenia patients, extending the disease relevance of our findings. Our data provide support for a model in which impaired synaptic vesicle cycling represents a critical node for disease pathologies underlying the cognitive deficits in schizophrenia.
Figures


References
-
- Behan AT, Byrne C, Dunn MJ, Cagney G, Cotter DR. Proteomic analysis of membrane microdomain-associated proteins in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder reveals alterations in LAMP, STXBP1 and BASP1 protein expression. Mol Psychiatry. 2009;14:601–613. doi: 10.1038/mp.2008.7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Calabrese P. Neuropsychology of multiple sclerosis: an overview. J Neurol. 2006;253(Suppl 1):I10–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
