Odin (ANKS1A) modulates EGF receptor recycling and stability
- PMID: 23825523
- PMCID: PMC3692516
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064817
Odin (ANKS1A) modulates EGF receptor recycling and stability
Abstract
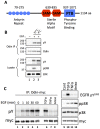
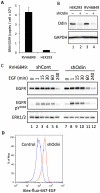
The ANKS1A gene product, also known as Odin, was first identified as a tyrosine-phosphorylated component of the epidermal growth factor receptor network. Here we show that Odin functions as an effector of EGFR recycling. In EGF-stimulated HEK293 cells tyrosine phosphorylation of Odin was induced prior to EGFR internalization and independent of EGFR-to-ERK signaling. Over-expression of Odin increased EGF-induced EGFR trafficking to recycling endosomes and recycling back to the cell surface, and decreased trafficking to lysosomes and degradation. Conversely, Odin knockdown in both HEK293 and the non-small cell lung carcinoma line RVH6849, which expresses roughly 10-fold more EGF receptors than HEK293, caused decreased EGFR recycling and accelerated trafficking to the lysosome and degradation. By governing the endocytic fate of internalized receptors, Odin may provide a layer of regulation that enables cells to contend with receptor cell densities and ligand concentration gradients that are physiologically and pathologically highly variable.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Schlessinger J (2002) Ligand-induced, receptor-mediated dimerization and activation of EGF receptor. Cell 110: 669–672. - PubMed
-
- Yarden Y (2001) The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer. signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur J Cancer 37 Suppl 4S3–8. - PubMed
-
- Sebastian S, Settleman J, Reshkin SJ, Azzariti A, Bellizzi A, et al. (2006) The complexity of targeting EGFR signalling in cancer: from expression to turnover. Biochim Biophys Acta 1766: 120–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

