Establishment of NOD/SCID mouse models of human hepatocellular carcinoma via subcutaneous transplantation of histologically intact tumor tissue
- PMID: 23825905
- PMCID: PMC3696707
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2013.05.02
Establishment of NOD/SCID mouse models of human hepatocellular carcinoma via subcutaneous transplantation of histologically intact tumor tissue
Abstract
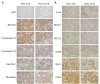
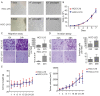
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most deadly human cancers, but it is very difficult to establish an animal model by using surgical specimens. In the present experiment, histologically intact fresh surgical specimens of HCC were subcutaneously transplanted in non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficienccy (NOD/SCID) mice. The biological characteristics of the original and the corresponding transplanted tumors and cell lines were investigated. The results showed that 5 new animal models and 2 primary cell lines were successfully established from surgical specimens. Hematoxylin-eosin staining showed that xenografts retained major histological features of the original surgical specimens. The two new cell lines had been cultivated for 3 years and successively passaged for more than 100 passages in vitro. The morphological characteristics and biologic features of the two cell lines were genetically similar to the original tumor. The subcutaneous transplant animal models with histologically intact tumor tissue and primary cell lines could be useful for in vivo and in vitro testing of anti-cancer drugs and be ideal models to study various biologic features of HCC.
Keywords: Animal model; hepatocellular carcinoma; subcutaneous transplantation; surgical specimens.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Establishment and characterization of in vivo human tumor models in the NOD/SCID/gamma(c)(null) mouse.Pathol Int. 2008 Sep;58(9):559-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02271.x. Pathol Int. 2008. PMID: 18801070
-
Nude mice model of human hepatocellular carcinoma via orthotopic implantation of histologically intact tissue.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Nov 1;10(21):3107-11. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i21.3107. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15457553 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a subcutaneous model of the human extrahepatic bile duct carcinoma in nude mice via transplantation of histologically intact tumor tissue.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Dec;23(4):661-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15743037
-
Metastatic human hepatocellular carcinoma models in nude mice and cell line with metastatic potential.World J Gastroenterol. 2001 Oct;7(5):597-601. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i5.597. World J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11819839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Application of NOD/SCID mice in research of experimental hematology - review].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Aug;16(4):964-8. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18718101 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
A Nude Mouse Model of Orthotopic Liver Transplantation of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma HCCLM3 Cell Xenografts and the Use of Imaging to Evaluate Tumor Progression.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Nov 18;25:8694-8703. doi: 10.12659/MSM.917648. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31736477 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Xenografts Established From Needle Biopsies Preserve the Characteristics of the Originating Tumors.Hepatol Commun. 2019 May 6;3(7):971-986. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1365. eCollection 2019 Jul. Hepatol Commun. 2019. PMID: 31334445 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and characterization of a highly metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma cell line.Bioengineered. 2024 Dec;15(1):2296775. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2023.2296775. Epub 2024 Jan 7. Bioengineered. 2024. PMID: 38184822 Free PMC article.
-
ESTABLISHMENT AND EVALUATION OF ORTHOTOPIC HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA AND DRUG-INDUCED HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA IN MICE WITH SPLEEN-DEFICIENCY SYNDROME IN TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2016 Nov 23;14(1):165-173. doi: 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i1.18. eCollection 2017. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 28480394 Free PMC article.
-
State-of-the-Art Liver Cancer Organoids: Modeling Cancer Stem Cell Heterogeneity for Personalized Treatment.BioDrugs. 2025 Mar;39(2):237-260. doi: 10.1007/s40259-024-00702-0. Epub 2025 Jan 18. BioDrugs. 2025. PMID: 39826071 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wu L, Tang ZY, Li Y. Experimental models of hepatocellular carcinoma: developments and evolution. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2009;135:969-81 - PubMed
-
- Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, et al. A decade’s studies on metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2004;130:187-96 - PubMed
-
- Pisani P, Parkin DM, Bray F, et al. Erratum: Estimates of the worldwide mortality from 25 cancers in 1990. Int J Cancer 1999;83:870-73 - PubMed
-
- Ochoa-Callejero L, Toshkov I, Menne S, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in the woodchuck model of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Med Virol. 2013 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
