Cost-effectiveness of dutasteride-tamsulosin combination therapy for the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: A Canadian model based on the CombAT trial
- PMID: 23826050
- PMCID: PMC3699085
- DOI: 10.5489/cuaj.12131
Cost-effectiveness of dutasteride-tamsulosin combination therapy for the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: A Canadian model based on the CombAT trial
Abstract
Introduction: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is common in men 50 years old and older. The main treatment options are alpha-blockers (such as tamsulosin), which reduce symptoms, and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (such as dutasteride), which reduce symptoms and slow disease progression. Clinical studies have demonstrated that dutasteride-tamsulosin combination therapy is more effective than either monotherapy to treat symptomatic BPH. We studied the cost-effectiveness in Canada of the dutasteride (0.5 mg/day) and tamsulosin (0.4 mg/day) combination compared with tamsulosin or dutasteride monotherapy.
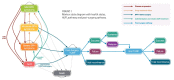
Methods: A Markov model was developed which follows a cohort of male BPH patients ≥50 with moderate to severe lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). The model estimates costs to the Canadian health care system and outcomes (in terms of quality adjusted life years [QALYs]) at 10 years and over a patient's lifetime. The dutasteride-tamsulosin combination was compared to each of tamsulosin monotherapy and dutasteride monotherapy.
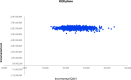
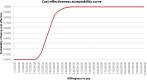
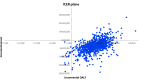
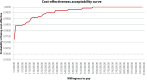
Results: Compared with tamsulosin, the combination was more costly and produced better patient outcomes. Over a lifetime, the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was CAN$25 437 per QALY gained. At a willingness to pay CAN$50 000 per QALY, the probability of combination therapy being cost-effective was 99.6%. Compared with dutasteride, the combination therapy was the dominant option from year 2, offering improved patient outcomes at lower cost. The probability that combination therapy is more cost-effective than dutasteride was 99.8%.
Conclusion: Combination therapy offers important clinical benefits for patients with symptomatic BPH, and there is a high probability that it is cost-effective in the Canadian health care system relative to either monotherapy.
Figures
Comment in
- Can Urol Assoc J. 7(5-6):e446.
Similar articles
-
Fixed-dose combination therapy with dutasteride and tamsulosin in the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia.Ther Adv Urol. 2016 Feb;8(1):19-28. doi: 10.1177/1756287215607419. Ther Adv Urol. 2016. PMID: 26834837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cost-effectiveness of single-dose tamsulosin and dutasteride combination therapy compared with tamsulosin monotherapy in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia in the UK.BJU Int. 2013 Sep;112(5):638-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11659.x. Epub 2013 Jan 28. BJU Int. 2013. PMID: 23356792
-
The effects of combination therapy with dutasteride and tamsulosin on clinical outcomes in men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: 4-year results from the CombAT study.Eur Urol. 2010 Jan;57(1):123-31. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.09.035. Epub 2009 Sep 19. Eur Urol. 2010. PMID: 19825505 Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of baseline variables on changes in International Prostate Symptom Score after combined therapy with dutasteride plus tamsulosin or either monotherapy in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms: 4-year results of the CombAT study.BJU Int. 2014 Apr;113(4):623-35. doi: 10.1111/bju.12500. Epub 2014 Jan 9. BJU Int. 2014. PMID: 24127818 Clinical Trial.
-
Dutasteride/tamsulosin: in benign prostatic hyperplasia.Drugs Aging. 2012 May 1;29(5):405-19. doi: 10.2165/11208920-000000000-00000. Drugs Aging. 2012. PMID: 22550968 Review.
Cited by
-
Fexapotide triflutate vs oral pharmacotherapy as initial therapy for moderate-to-severe benign prostate hyperplasia patients: a cost-effectiveness analysis.BMC Urol. 2022 May 13;22(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12894-022-01025-4. BMC Urol. 2022. PMID: 35550071 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of a fixed-dose combination of solifenacin and oral controlled adsorption system formulation of tamsulosin in men with lower urinary tract symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia.BMC Urol. 2015 May 9;15:41. doi: 10.1186/s12894-015-0031-8. BMC Urol. 2015. PMID: 25956727 Free PMC article.
-
Cost analysis of fixed-dose combination of dutasteride and tamsulosin compared with concomitant dutasteride and tamsulosin monotherapy in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia in Canada.Can Urol Assoc J. 2014 Jan-Feb;8(1-2):E1-7. doi: 10.5489/cuaj.755. Can Urol Assoc J. 2014. PMID: 24454593 Free PMC article.
-
Economic Evaluation of Combination Therapy Versus Monotherapy for Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Hong Kong.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Oct 16;9:1078. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01078. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30386234 Free PMC article.
-
Fixed-dose combination therapy with dutasteride and tamsulosin in the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia.Ther Adv Urol. 2016 Feb;8(1):19-28. doi: 10.1177/1756287215607419. Ther Adv Urol. 2016. PMID: 26834837 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lourenco T, Armstrong N, N’Dow J, et al. Systematic review and economic modelling of effectiveness and cost utility of surgical treatments for men with benign prostatic enlargement. Health Technol Assess. 2008;12:iii, ix–x, 1–146, 169–515. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
