Complete genome analysis of three Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in China for insight into the diversification of drug resistance elements
- PMID: 23826102
- PMCID: PMC3691203
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066584
Complete genome analysis of three Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in China for insight into the diversification of drug resistance elements
Abstract
Background: The emergence and rapid spreading of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii strains has become a major health threat worldwide. To better understand the genetic recombination related with the acquisition of drug-resistant elements during bacterial infection, we performed complete genome analysis on three newly isolated multidrug-resistant A. baumannii strains from Beijing using next-generation sequencing technology.
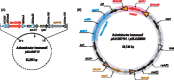
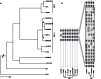
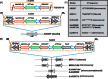
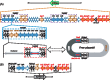
Methodologies/principal findings: Whole genome comparison revealed that all 3 strains share some common drug resistant elements including carbapenem-resistant bla OXA-23 and tetracycline (tet) resistance islands, but the genome structures are diversified among strains. Various genomic islands intersperse on the genome with transposons and insertions, reflecting the recombination flexibility during the acquisition of the resistant elements. The blood-isolated BJAB07104 and ascites-isolated BJAB0868 exhibit high similarity on their genome structure with most of the global clone II strains, suggesting these two strains belong to the dominant outbreak strains prevalent worldwide. A large resistance island (RI) of about 121-kb, carrying a cluster of resistance-related genes, was inserted into the ATPase gene on BJAB07104 and BJAB0868 genomes. A 78-kb insertion element carrying tra-locus and bla OXA-23 island, can be either inserted into one of the tniB gene in the 121-kb RI on the chromosome, or transformed to conjugative plasmid in the two BJAB strains. The third strains of this study, BJAB0715, which was isolated from spinal fluid, exhibit much more divergence compared with above two strains. It harbors multiple drug-resistance elements including a truncated AbaR-22-like RI on its genome. One of the unique features of this strain is that it carries both bla OXA-23 and bla OXA-58 genes on its genome. Besides, an Acinetobacter lwoffii adeABC efflux element was found inserted into the ATPase position in BJAB0715.
Conclusions: Our comparative analysis on currently completed Acinetobacter baumannii genomes revealed extensive and dynamic genome organizations, which may facilitate the bacteria to acquire drug-resistance elements into their genomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Kwon KT, Oh WS, Song JH, Chang HH, Jung SI (2007) Impact of imipenem resistance on mortality in patients with Acinetobacter bacteraemia. J Antimicrob Chemother 59: 525–530. - PubMed
-
- Falagas ME, Karveli EA (2007) The changing global epidemiology of Acinetobacter baumannii infections: a development with major public health implications. Clin Microbiol Infect 13: 117–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

