Chromosomal Locations of 5S and 45S rDNA in Gossypium Genus and Its Phylogenetic Implications Revealed by FISH
- PMID: 23826377
- PMCID: PMC3695094
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068207
Chromosomal Locations of 5S and 45S rDNA in Gossypium Genus and Its Phylogenetic Implications Revealed by FISH
Abstract
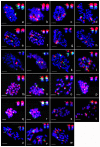
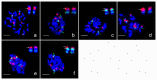
We investigated the locations of 5S and 45S rDNA in Gossypium diploid A, B, D, E, F, G genomes and tetraploid genome (AD) using multi-probe fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) for evolution analysis in Gossypium genus. The rDNA numbers and sizes, and synteny relationships between 5S and 45S were revealed using 5S and 45S as double-probe for all species, and the rDNA-bearing chromosomes were identified for A, D and AD genomes with one more probe that is single-chromosome-specific BAC clone from G. hirsutum (A1D1). Two to four 45S and one 5S loci were found in diploid-species except two 5S loci in G. incanum (E4), the same as that in tetraploid species. The 45S on the 7th and 9th chromosomes and the 5S on the 9th chromosomes seemed to be conserved in A, D and AD genomes. In the species of B, E, F and G genomes, the rDNA numbers, sizes, and synteny relationships were first reported in this paper. The rDNA pattern agrees with previously reported phylogenetic history with some disagreements. Combined with the whole-genome sequencing data from G. raimondii (D5) and the conserved cotton karyotype, it is suggested that the expansion, decrease and transposition of rDNA other than chromosome rearrangements might occur during the Gossypium evolution.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Distribution of 5S and 18S-28S rDNA loci in a tetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) and its putative diploid ancestors.Chromosoma. 1996 Jul;105(1):55-61. doi: 10.1007/BF02510039. Chromosoma. 1996. PMID: 8662259
-
Individual chromosome assignment and chromosomal collinearity in Gossypium thurberi, G. trilobum and D subgenome of G. barbadense revealed by BAC-FISH.Genes Genet Syst. 2011;86(3):165-74. doi: 10.1266/ggs.86.165. Genes Genet Syst. 2011. PMID: 21952206
-
Comparative chromosomal localization of 45S and 5S rDNAs and implications for genome evolution in Cucumis.Genome. 2016 Jul;59(7):449-57. doi: 10.1139/gen-2015-0207. Epub 2016 May 11. Genome. 2016. PMID: 27334092
-
Species of the Sections Hedysarum and Multicaulia of the Genus Hedysarum (Fabaceae): Taxonomy, Distribution, Chromosomes, Genomes, and Phylogeny.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 3;25(15):8489. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158489. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39126057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and Evolution of Ribosomal Genes of Insect Chromosomes.Insects. 2024 Aug 4;15(8):593. doi: 10.3390/insects15080593. Insects. 2024. PMID: 39194798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Screening and chromosome localization of two cotton BAC clones.Comp Cytogenet. 2016 Jan 22;10(1):1-15. doi: 10.3897/CompCytogen.v10i1.5304. eCollection 2016. Comp Cytogenet. 2016. PMID: 27186333 Free PMC article.
-
Plant rDNA database: update and new features.Database (Oxford). 2014 Jun 30;2014:bau063. doi: 10.1093/database/bau063. Print 2014. Database (Oxford). 2014. PMID: 24980131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytogenetics and Consequences of Polyploidization on Different Biotic-Abiotic Stress Tolerance and the Potential Mechanisms Involved.Plants (Basel). 2022 Oct 12;11(20):2684. doi: 10.3390/plants11202684. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A telomere-to-telomere genome assembly of cotton provides insights into centromere evolution and short-season adaptation.Nat Genet. 2025 Apr;57(4):1031-1043. doi: 10.1038/s41588-025-02130-4. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Nat Genet. 2025. PMID: 40097785
-
Chromosome Painting Based on Bulked Oligonucleotides in Cotton.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jun 30;11:802. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00802. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32695125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Endrizzi JE, Turcotte EL, Kohel RJ (1985) Genetics, cytogenetics, and evolution of Gossypium . Adv Genet 23: 271-375. doi:10.1016/S0065-2660(08)60515-5. - DOI
-
- Stewart JMcD (1995) Potential for crop improvement with exotic germ plasm and genetic engineering. In: Constable GA, Forrester NW. Challenging the future: Proceedings of the World Cotton Research. Melbourne. pp. 313-327.
-
- Leitch IJ, Heslop-Harrison JS (1992) Physical mapping of the 18S-5.8-26S rRNA genes in barley by in situ hybridization. Genome 35: 1013-1018. doi:10.1139/g92-155. - DOI
-
- Linde-Laursen I, Ibsen E, Von Bothmer R, Giese H (1992) Physical localization of active and inactive rRNA gene loci in Hordeum marinum ssp. gussoneanum (4×) by in situ hybridization. Genome 35: 1032-1036. doi:10.1139/g92-158. - DOI
-
- Raina SN, Mukai Y (1999) Detection of a variable number of 18S-5.8S-26S and 5S ribosomal DNA loci by fluorescent in situ hybridization in diploid and tetraploid Arachis species. Genome 42: 52-59. doi:10.1139/g98-092. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

