Mechanism of immune tolerance induced by donor derived immature dendritic cells in rat high-risk corneal transplantation
- PMID: 23826517
- PMCID: PMC3693004
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2013.03.03
Mechanism of immune tolerance induced by donor derived immature dendritic cells in rat high-risk corneal transplantation
Abstract
Aim: To study the role of immature dendritic cells (imDCs) on immune tolerance in rat penetrating keratoplasty (PKP) in high-risk eyes and to investigate the mechanism of immune hyporesponsiveness induced by donor-derived imDCs.
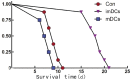
Methods: Seventy-five SD rats (recipient) and 39 Wistar rats (donor) were randomly divided into 3 groups: control, imDC and mature dendritic cell (mDC) group respectively. Using a model of orthotopic corneal transplantation in which allografts were placed in neovascularized high-risk eyes of recipient rat. Corneal neovascularization was induced by alkaline burn in the central cornea of recipient rat. Recipients in imDC group or mDC group were injected donor bone marrow-derived imDCs or mDCs of 1×10(6) respectively 1 week before corneal transplantation via tail vein. Control rat received the same volume of PBS. In each group, 16 recipients were kept for determination of survival time and other 9 recipients were executed on day 3, 7 and 14 after transplantation. Cornea was harvested for hematoxylin-eosin staining and acute rejection evaluation, Western blot was used to detect the expression level of Foxp3.
Results: The mean survival time of imDC group was significantly longer than that of control and mDC groups (all P<0.05). The expression level of Foxp3 on CD4(+)CD25(+)T cells of imDC group (2.24±0.18) was significantly higher than that in the control (1.68±0.09) and mDC groups (1.46±0.13) (all P<0.05).
Conclusion: Donor-derived imDC is an effective treatment in inducing immune hyporesponsiveness in rat PKP. The mechanism of immune tolerance induced by imDC might be inhibit T lymphocytes responsiveness by regulatory T cells.
Keywords: high-risk keratoplasty; immature dendritic cell; regulatory T cells.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Mechanism of immune hyporesponsiveness induced by recipient- derived immature dendritic cells in liver transplantation rat.Chin Med Sci J. 2011 Mar;26(1):28-35. doi: 10.1016/s1001-9294(11)60016-3. Chin Med Sci J. 2011. PMID: 21496420
-
Rapamycin combined with donor immature dendritic cells promotes liver allograft survival in association with CD4(+) CD25(+) Foxp3(+) regulatory T cell expansion.Hepatol Res. 2012 Feb;42(2):192-202. doi: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2011.00909.x. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Hepatol Res. 2012. PMID: 22103959
-
Rapamycin Combined with Immature Dendritic Cells Attenuates Obliterative Bronchiolitis in Trachea Allograft Rats by Regulating the Balance of Regulatory and Effector T Cells.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2015;167(3):177-85. doi: 10.1159/000437207. Epub 2015 Aug 22. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26302996
-
Prolonged survival of donor-specific rat intestinal allograft by administration of bone-marrow-derived immature dendritic cells.Transpl Immunol. 2005 Mar;14(1):17-20. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2004.12.002. Epub 2005 Jan 21. Transpl Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15814277
-
Prolonged survival effects induced by immature dendritic cells and regulatory T cells in a rat liver transplantation model.Mol Immunol. 2016 Nov;79:92-97. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2016.10.004. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Mol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27764710
Cited by
-
Rhamnazin attenuates inflammation and inhibits alkali burn-induced corneal neovascularization in rats.RSC Adv. 2018 Jul 27;8(47):26696-26706. doi: 10.1039/c8ra03159b. eCollection 2018 Jul 24. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35541079 Free PMC article.
-
Immune tolerance of mice allogenic tooth transplantation induced by immature dendritic cells.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Apr 15;8(4):5254-62. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26131099 Free PMC article.
-
High-risk Corneal Transplantation: Recent Developments and Future Possibilities.Transplantation. 2019 Dec;103(12):2468-2478. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002938. Transplantation. 2019. PMID: 31765363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Observation on ultrastructure and histopathology of cornea following femtosecond laser-assisted deep lamellar keratoplasty for acute corneal alkaline burns.Int J Ophthalmol. 2016 Apr 18;9(4):481-6. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2016.04.01. eCollection 2016. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27162716 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Immune Cell Diversity and Heterogeneity in Corneal Graft Survival: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2021 Oct 12;10(20):4667. doi: 10.3390/jcm10204667. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34682792 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Santos LN, de Moura LR, Fernandes BF, Cheema DP, Burnier MN., Jr Histopathological study of delayed regraft after corneal graft failure. Cornea. 2011;30(2):167–170. - PubMed
-
- Fasolo A, Capuzzo C, Fornea M, Franch A, Birattari F, Carito G. Risk factors for graft failure after penetrating keratoplasty: 5-year follow-up from the corneal transplant epidemiological study. Cornea. 2011;30(12):1328–1335. - PubMed
-
- Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F. Regulation of T cell immunity by dendritic cells. Cell. 2001;106(3):263–6. - PubMed
-
- Steinman RM. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity: enhancing the efficiency of antigen presentation. Mt Sinai J Med. 2001;68(3):160–166. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
