Type 2 immunity and wound healing: evolutionary refinement of adaptive immunity by helminths
- PMID: 23827958
- PMCID: PMC3789590
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3476
Type 2 immunity and wound healing: evolutionary refinement of adaptive immunity by helminths
Abstract
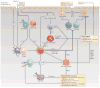
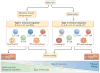
Helminth-induced type 2 immune responses, which are characterized by the T helper 2 cell-associated cytokines interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13, mediate host protection through enhanced tissue repair, the control of inflammation and worm expulsion. In this Opinion article, we consider type 2 immunity in the context of helminth-mediated tissue damage. We examine the relationship between the control of helminth infection and the mechanisms of wound repair, and we provide a new understanding of the adaptive type 2 immune response and its contribution to both host tolerance and resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: see Web version for details.
Figures

References
-
- Artis D, Maizels RM, Finkelman FD. Forum: Immunology: Allergy challenged. Nature. 2012;484:458–459. - PubMed
-
- Deter J, Cosson JF, Chaval Y, Charbonnel N, Morand S. The intestinal nematode Trichuris arvicolae affects the fecundity of its host, the common vole Microtus arvalis. Parasitol Res. 2007;101:1161–1164. - PubMed
-
- Coop RL, Kyriazakis I. Influence of host nutrition on the development and consequences of nematode parasitism in ruminants. Trends Parasitol. 2001;17:325–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

