DHX34 and NBAS form part of an autoregulatory NMD circuit that regulates endogenous RNA targets in human cells, zebrafish and Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 23828042
- PMCID: PMC3783168
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt585
DHX34 and NBAS form part of an autoregulatory NMD circuit that regulates endogenous RNA targets in human cells, zebrafish and Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
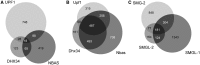
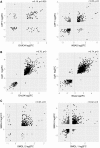
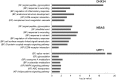
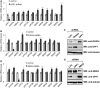
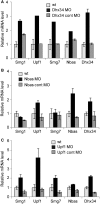
The nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) pathway selectively degrades mRNAs harboring premature termination codons but also regulates the abundance of cellular RNAs. We sought to identify transcripts that are regulated by two novel NMD factors, DHX34 and neuroblastoma amplified sequence (NBAS), which were identified in a genome-wide RNA interference screen in Caenorhabditis elegans and later shown to mediate NMD in vertebrates. We performed microarray expression profile analysis in human cells, zebrafish embryos and C. elegans that were individually depleted of these factors. Our analysis revealed that a significant proportion of genes are co-regulated by DHX34, NBAS and core NMD factors in these three organisms. Further analysis indicates that NMD modulates cellular stress response pathways and membrane trafficking across species. Interestingly, transcripts encoding different NMD factors were sensitive to DHX34 and NBAS depletion, suggesting that these factors participate in a conserved NMD negative feedback regulatory loop, as was recently described for core NMD factors. In summary, we find that DHX34 and NBAS act in concert with core NMD factors to co-regulate a large number of endogenous RNA targets. Furthermore, the conservation of a mechanism to tightly control NMD homeostasis across different species highlights the importance of the NMD response in the control of gene expression.
Figures

References
-
- Chang YF, Imam JS, Wilkinson MF. The nonsense-mediated decay RNA surveillance pathway. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2007;76:51–74. - PubMed
-
- Palacios IM, Kervestin S, Jacobson A. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: from mechanistic insights to impacts on human health. Brief. Funct. Genomics. 2013;12:700–712. - PubMed
-
- Bhuvanagiri M, Schlitter AM, Hentze MW, Kulozik AE. NMD: RNA biology meets human genetic medicine. Biochem. J. 2010;430:365–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

