Transcriptional properties of mammalian elongin A and its role in stress response
- PMID: 23828199
- PMCID: PMC3750133
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.496703
Transcriptional properties of mammalian elongin A and its role in stress response
Abstract
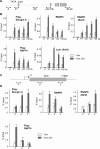
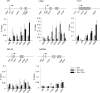
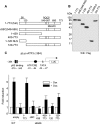
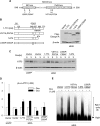
Elongin A was shown previously to be capable of potently activating the rate of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) transcription elongation in vitro by suppressing transient pausing by the enzyme at many sites along DNA templates. The role of Elongin A in RNAPII transcription in mammalian cells, however, has not been clearly established. In this report, we investigate the function of Elongin A in RNAPII transcription. We present evidence that Elongin A associates with the IIO form of RNAPII at sites of newly transcribed RNA and is relocated to dotlike domains distinct from those containing RNAPII when cells are treated with the kinase inhibitor 5,6-dichloro-1-β-d-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole. Significantly, Elongin A is required for maximal induction of transcription of the stress response genes ATF3 and p21 in response to several stimuli. Evidence from structure-function studies argues that Elongin A transcription elongation activity, but not its ubiquitination activity, is most important for its function in induction of transcription of ATF3 and p21. Taken together, our data provide new insights into the function of Elongin A in RNAPII transcription and bring to light a previously unrecognized role for Elongin A in the regulation of stress response genes.
Keywords: ATF3; Elongin A; Gene Regulation; Mammal; RNA Polymerase II; Stress Response; Transcription Elongation Factors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elongin A regulates transcription in vivo through enhanced RNA polymerase processivity.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100170. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015876. Epub 2020 Dec 13. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33298525 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and proteomic analysis of transcription factor TFII-I reveals insight into the response to cellular stress.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jul;42(12):7625-41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku467. Epub 2014 May 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24875474 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factors TFIIF, ELL, and Elongin negatively regulate SII-induced nascent transcript cleavage by non-arrested RNA polymerase II elongation intermediates.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jun 22;276(25):23109-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101445200. Epub 2001 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11259417
-
The RNA polymerase II elongation complex.FASEB J. 1995 Nov;9(14):1419-28. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.9.14.7589983. FASEB J. 1995. PMID: 7589983 Review.
-
The RNA polymerase II general elongation factors.Trends Biochem Sci. 1996 Sep;21(9):351-5. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996. PMID: 8870500 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Def1 interacts with TFIIH and modulates RNA polymerase II transcription.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Dec 12;114(50):13230-13235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707955114. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 29180430 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of p21CIP1 protein and cell cycle arrest after inhibition of Aurora B kinase is attributed to aneuploidy and reactive oxygen species.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jun 6;289(23):16072-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.555060. Epub 2014 Apr 29. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24782314 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA DLGAP1-AS2 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis by regulating the Trim21/ELOA/LHPP axis in colorectal cancer.Mol Cancer. 2022 Nov 14;21(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01675-w. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36376892 Free PMC article.
-
The hunt for RNA polymerase II elongation factors: a historical perspective.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019 Sep;26(9):771-776. doi: 10.1038/s41594-019-0283-1. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31439940 Review.
-
Regulation of RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation and Elongation by Transcription Factor TFII-I.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 13;8:681550. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.681550. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34055891 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shilatifard A., Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. (2003) The RNA polymerase II elongation complex. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72, 693–715 - PubMed
-
- Sims R. J., 3rd, Belotserkovskaya R., Reinberg D. (2004) Elongation by RNA polymerase II: the short and long of it. Genes Dev. 18, 2437–2468 - PubMed
-
- Wada T., Takagi T., Yamaguchi Y., Ferdous A., Imai T., Hirose S., Sugimoto S., Yano K., Hartzog G. A., Winston F., Buratowski S., Handa H. (1998) DSIF, a novel transcription elongation factor that regulates RNA polymerase II processivity, is composed of human Spt4 and Spt5 homologs. Genes Dev. 12, 343–356 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi Y., Takagi T., Wada T., Yano K., Furuya A., Sugimoto S., Hasegawa J., Handa H. (1999) NELF, a multisubunit complex containing RD, cooperates with DSIF to repress RNA polymerase II elongation. Cell 97, 41–51 - PubMed
-
- Saunders A., Core L. J., Lis J. T. (2006) Breaking barriers to transcription elongation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 557–567 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

