Effects of phosphorylation on the structure and backbone dynamics of the intrinsically disordered connexin43 C-terminal domain
- PMID: 23828237
- PMCID: PMC3750180
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.454389
Effects of phosphorylation on the structure and backbone dynamics of the intrinsically disordered connexin43 C-terminal domain
Abstract
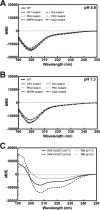
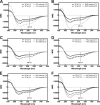
Phosphorylation of the connexin43 C-terminal (Cx43CT) domain regulates gap junction intercellular communication. However, an understanding of the mechanisms by which phosphorylation exerts its effects is lacking. Here, we test the hypothesis that phosphorylation regulates Cx43 gap junction intercellular communication by mediating structural changes in the C-terminal domain. Circular dichroism and nuclear magnetic resonance were used to characterize the effects of phosphorylation on the secondary structure and backbone dynamics of soluble and membrane-tethered Cx43CT domains. Cx43CT phospho-mimetic isoforms, which have Asp substitutions at specific Ser/Tyr sites, revealed phosphorylation alters the α-helical content of the Cx43CT domain only when attached to the membrane. The changes in secondary structure are due to variations in the conformational preference and backbone flexibility of residues adjacent and distal to the site(s) of modification. In addition to the known direct effects of phosphorylation on molecular partner interactions, the data presented here suggest phosphorylation may also indirectly regulate binding affinity by altering the conformational preference of the Cx43CT domain.
Keywords: Circular Dichroism (CD); Gap Junctions; Nuclear Magnetic Resonance; Phosphorylation; Protein Dynamics.
Figures
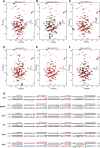

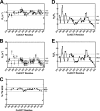
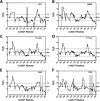
References
-
- Kumar N. M., Gilula N. B. (1996) The gap junction communication channel. Cell 84, 381–388 - PubMed
-
- Laird D. W. (2008) Closing the gap on autosomal dominant connexin-26 and connexin-43 mutants linked to human disease. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 2997–3001 - PubMed
-
- Dobrowolski R., Willecke K. (2009) Connexin-caused genetic diseases and corresponding mouse models. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 11, 283–295 - PubMed
-
- Unger V. M., Kumar N. M., Gilula N. B., Yeager M. (1999) Three-dimensional structure of a recombinant gap junction membrane channel. Science 283, 1176–1180 - PubMed
-
- Maeda S., Nakagawa S., Suga M., Yamashita E., Oshima A., Fujiyoshi Y., Tsukihara T. (2009) Structure of the connexin 26 gap junction channel at 3.5 Å resolution. Nature 458, 597–602 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

