Role of Fas-associated death domain-containing protein (FADD) phosphorylation in regulating glucose homeostasis: from proteomic discovery to physiological validation
- PMID: 23828893
- PMCID: PMC3790283
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M113.029306
Role of Fas-associated death domain-containing protein (FADD) phosphorylation in regulating glucose homeostasis: from proteomic discovery to physiological validation
Abstract
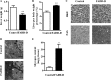
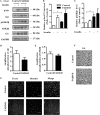
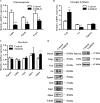
Fas-associated death domain-containing protein (FADD), a classical apoptotic signaling adaptor, participates in different nonapoptotic processes regulated by its phosphorylation. However, the influence of FADD on metabolism, especially glucose homeostasis, has not been evaluated to date. Here, using both two-dimensional electrophoresis and liquid chromatography linked to tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS), we found that glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, and gluconeogenesis were dysregulated because of FADD phosphorylation, both in MEFs and liver tissue of the mice bearing phosphorylation-mimicking mutation form of FADD (FADD-D). Further physiological studies showed that FADD-D mice exhibited lower blood glucose, enhanced glucose tolerance, and increased liver glycogen content without alterations in insulin sensitivity. Moreover, investigations on the molecular mechanisms revealed that, under basal conditions, FADD-D mice had elevated phosphorylation of Akt with alterations in its downstream signaling, leading to increased glycogen synthesis and decreased gluconeogenesis. Thus, we uncover a novel role of FADD in the regulation of glucose homeostasis by proteomic discovery and physiological validation.
Figures



References
-
- Boldin M. P., Varfolomeev E. E., Pancer Z., Mett I. L., Camonis J. H., Wallach D. (1995) A novel protein that interacts with the death domain of Fas/APO1 contains a sequence motif related to the death domain. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 7795–7798 - PubMed
-
- Chinnaiyan A. M., Orourke K., Tewari M., Dixit V. M. (1995) FADD, A Novel Death Domain-Containing Protein, Interacts With the Death Domain of Fas and Initiates Apoptosis. Cell. 81, 505–512 - PubMed
-
- Kim P. K., Dutra A. S., Chandrasekharappa S. C., Puck J. M. (1996) Genomic structure and mapping of human FADD, an intracellular mediator of lymphocyte apoptosis. J. Immunol. 157, 5461–5466 - PubMed
-
- Schneider P., Thome M., Burns K., Bodmer J. L., Hofmann K., Kataoka T., Holler N., Tschopp J. (1997) TRAIL receptors 1 (DR4) and 2 (DR5) signal FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate NF-kappaB. Immunity 7, 831–836 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

