Prophylaxis with erythropoietin versus placebo reduces acute kidney injury and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a randomized, double-blind controlled trial
- PMID: 23829828
- PMCID: PMC3704968
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2369-14-136
Prophylaxis with erythropoietin versus placebo reduces acute kidney injury and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a randomized, double-blind controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury (CSA-AKI) is a common complication following coronary bypass graft (CABG) surgery. Multi-factorial causes of CSA-AKI involve oxidative stress and inflammation. Erythropoietin (EPO) has been shown from many studies to have a reno-protective effect. The present study was conducted to examine the role of EPO in preventing CSA-AKI.
Methods: This prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was conducted in the Cardiovascular and Thoracic Unit. One hundred patients randomly received either 200 U/kg of rHuEPO (n = 50) or saline (n = 50) intravenously three days before operation, and rHuEPO 100 U/kg or saline at operation time. The serum creatinine (SCr), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocaline (NGAL) were measured in order to evaluate renal injury following CABG.
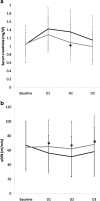
Results: The incidence of CSA-AKI was significantly lower in rHuEPO group (14%) when compared with the placebo group (38%; p < 0.01). The mean intensive care unit (ICU) and hospital stays of the rHuEPO group were significantly shorter than the placebo group (p < 0.01). Postoperative increases in SCr and decreases in eGFR were significantly lower in the rHuEPO group than the placebo group (p < 0.05). The mean urine NGAL in rHuEPO group was significantly lower than the placebo group at 3 hr, 6 hr, 12 hr and 18 hr after CABG (p < 0.05), respectively.
Conclusions: Prophylaxis administration with intravenous rHuEPO before cardiac surgery decreased the incidence of CSA-AKI and urine NGAL with reduced days in ICU and hospital in elective CABG patients.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01066351.
Figures
References
-
- Mangano CM, Diamondstone LS, Ramsay JG, Aggarwal A, Herskowitz A, Mangano DT. Renal dysfunction after myocardial revascularization: risk factors, adverse outcomes, and hospital resource utilization. The Multicenter Study of Perioperative Ischemia Research Group. Ann Intern Med. 1998;128(3):194–203. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-128-3-199802010-00005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shroyer AL, Coombs LP, Peterson ED, Eiken MC, DeLong ER, Chen A, Ferguson TB Jr, Grover FL, Edwards FH. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons: 30-day operative mortality and morbidity risk models. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;75(6):1856–1864. doi: 10.1016/S0003-4975(03)00179-6. discussion 1864–1855. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

