Severe community-acquired pneumonia
- PMID: 23830654
- PMCID: PMC7126707
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccc.2013.03.009
Severe community-acquired pneumonia
Abstract
Severe community-acquired pneumonia necessitating intensive care unit admission is associated with high morbidity, mortality, and health-care cost. This review article serves to summarize the epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of this common life-threatening condition. Current practice guidelines as well as the role of several scoring systems (such as the PSI, CURB-65, and IDSA/ATS criteria) used to predict CAP severity, prognosis, and site of care are reviewed. In addition, common complications and prevention strategies are discussed.
Keywords: Community-acquired pneumonia; Intensive care; Lung; Pulmonary sepsis; Respiratory failure.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
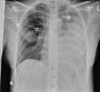
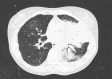
References
-
- File T.M., Jr., Marrie T.J. Burden of community-acquired pneumonia in North American adults. Postgrad Med. 2010;122:130–141. - PubMed
-
- Heron M., Hoyert D.L., Murphy S.L. Deaths: final data for 2006. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2009;57:1–134. - PubMed
-
- Minino A.M., Murphy S.L., Xu J. Deaths: final data for 2008. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2011;59:1–126. - PubMed
-
- Average length of stay and days of care – Number and rate of discharges by first-listed diagnostic categories. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2009. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/pneumonia.htm. Accessed October 20, 2012.
-
- Grossman R.F., Rotschafer J.C., Tan J.S. Antimicrobial treatment of lower respiratory tract infections in the hospital setting. Am J Med. 2005;118(Suppl 7A):29S–38S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

