Oxysterol binding to the extracellular domain of Smoothened in Hedgehog signaling
- PMID: 23831757
- PMCID: PMC3749252
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1290
Oxysterol binding to the extracellular domain of Smoothened in Hedgehog signaling
Abstract
Oxysterols bind the seven-transmembrane protein Smo (Smo) and potently activate vertebrate Hedgehog (Hh) signaling, a pathway essential in embryonic development, adult stem cell maintenance and cancer. It is unknown, however, whether oxysterols are important for normal vertebrate Hh signaling and whether antagonizing oxysterols can inhibit the Hh pathway. We developed azasterols that block Hh signaling by binding the oxysterol-binding site of Smo. We show that the binding site for oxysterols and azasterols maps to the extracellular, cysteine-rich domain of Smo and is completely separable from the site bound by other small-molecule modulators, located within the heptahelical bundle of Smo. Smo mutants in which oxysterol binding is abolished no longer respond to oxysterols and cannot be maximally activated by the Hh ligand. Our results show that oxysterol binding to vertebrate Smo is required for normal Hh signaling and that targeting the oxysterol-binding site is an effective strategy to inhibit Smo.
Figures
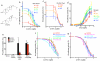



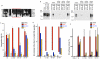

References
-
- Lum L, Beachy PA. The Hedgehog response network: sensors, switches, and routers. Science. 2004;304:1755–1759. - PubMed
-
- Ingham PW, McMahon AP. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes & development. 2001;15:3059–3087. doi:10.1101/gad.938601. - PubMed
-
- Taipale J, Cooper MK, Maiti T, Beachy PA. Patched acts catalytically to suppress the activity of Smoothened. Nature. 2002;418:892–897. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- PubChem-Substance/163620657
- PubChem-Substance/163620658
- PubChem-Substance/163620659
- PubChem-Substance/163620660
- PubChem-Substance/163620661
- PubChem-Substance/163620662
- PubChem-Substance/163620663
- PubChem-Substance/163620664
- PubChem-Substance/163620665
- PubChem-Substance/163620666
- PubChem-Substance/163620667
- PubChem-Substance/163620668
- PubChem-Substance/163620669
- PubChem-Substance/163620670
- PubChem-Substance/163620671
- PubChem-Substance/163620672
- PubChem-Substance/163620673
- PubChem-Substance/163620674
- PubChem-Substance/163620675
- PubChem-Substance/163620676
- PubChem-Substance/163620677
- PubChem-Substance/163620678
- PubChem-Substance/163620679
- PubChem-Substance/163620680
- PubChem-Substance/163620681
- PubChem-Substance/163620682
- PubChem-Substance/163620683
- PubChem-Substance/163620684
- PubChem-Substance/163620685
- PubChem-Substance/163620686
- PubChem-Substance/163620687
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

