GluN2B in corticostriatal circuits governs choice learning and choice shifting
- PMID: 23831965
- PMCID: PMC3725191
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3457
GluN2B in corticostriatal circuits governs choice learning and choice shifting
Abstract
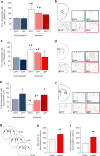
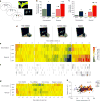
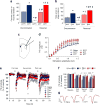
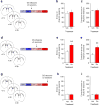
A choice that reliably produces a preferred outcome can be automated to liberate cognitive resources for other tasks. Should an outcome become less desirable, behavior must adapt in parallel or it becomes perseverative. Corticostriatal systems are known to mediate choice learning and flexibility, but the molecular mechanisms of these processes are not well understood. We integrated mouse behavioral, immunocytochemical, in vivo electrophysiological, genetic and pharmacological approaches to study choice. We found that the dorsal striatum (DS) was increasingly activated with choice learning, whereas reversal of learned choice engaged prefrontal regions. In vivo, DS neurons showed activity associated with reward anticipation and receipt that emerged with learning and relearning. Corticostriatal or striatal deletion of Grin2b (encoding the NMDA-type glutamate receptor subunit GluN2B) or DS-restricted GluN2B antagonism impaired choice learning, whereas cortical Grin2b deletion or OFC GluN2B antagonism impaired shifting. Our convergent data demonstrate how corticostriatal GluN2B circuits govern the ability to learn and shift choice behavior.
Figures


References
-
- Middleton FA, Strick PL. Basal-ganglia ‘projections’ to the prefrontal cortex of the primate. Cereb Cortex. 2002;12:926–935. - PubMed
-
- Mainen ZF, Kepecs A. Neural representation of behavioral outcomes in the orbitofrontal cortex. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2009;19:84–91. - PubMed
-
- Montague PR, King-Casas B, Cohen JD. Imaging valuation models in human choice. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2006;29:417–448. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

