Multimodal immunogenic cancer cell death as a consequence of anticancer cytotoxic treatments
- PMID: 23832118
- PMCID: PMC3857623
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2013.84
Multimodal immunogenic cancer cell death as a consequence of anticancer cytotoxic treatments
Abstract
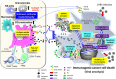
Apoptotic cell death generally characterized by a morphologically homogenous entity has been considered to be essentially non-immunogenic. However, apoptotic cancer cell death, also known as type 1 programmed cell death (PCD), was recently found to be immunogenic after treatment with several chemotherapeutic agents and oncolytic viruses through the emission of various danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). Extensive studies have revealed that two different types of immunogenic cell death (ICD) inducers, recently classified by their distinct actions in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, can reinitiate immune responses suppressed by the tumor microenvironment. Indeed, recent clinical studies have shown that several immunotherapeutic modalities including therapeutic cancer vaccines and oncolytic viruses, but not conventional chemotherapies, culminate in beneficial outcomes, probably because of their different mechanisms of ICD induction. Furthermore, interests in PCD of cancer cells have shifted from its classical form to novel forms involving autophagic cell death (ACD), programmed necrotic cell death (necroptosis), and pyroptosis, some of which entail immunogenicity after anticancer treatments. In this review, we provide a brief outline of the well-characterized DAMPs such as calreticulin (CRT) exposure, high-mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) release, which are induced by the morphologically distinct types of cell death. In the latter part, our review focuses on how emerging oncolytic viruses induce different forms of cell death and the combinations of oncolytic virotherapies with further immunomodulation by cyclophosphamide and other immunotherapeutic modalities foster dendritic cell (DC)-mediated induction of antitumor immunity. Accordingly, it is increasingly important to fully understand how and which ICD inducers cause multimodal ICD, which should aid the design of reasonably multifaceted anticancer modalities to maximize ICD-triggered antitumor immunity and eliminate residual or metastasized tumors while sparing autoimmune diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complementary induction of immunogenic cell death by oncolytic parvovirus H-1PV and gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer.J Virol. 2014 May;88(10):5263-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03688-13. Epub 2014 Feb 26. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24574398 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenic cell death in anticancer chemotherapy and its impact on clinical studies.Cancer Lett. 2018 Dec 1;438:17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.08.028. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 30217563 Review.
-
Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy.Nat Rev Cancer. 2012 Dec;12(12):860-75. doi: 10.1038/nrc3380. Epub 2012 Nov 15. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23151605 Review.
-
Targeting immunogenic cell death in cancer.Mol Oncol. 2020 Dec;14(12):2994-3006. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12851. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33179413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunogenic Apoptotic Cell Death and Anticancer Immunity.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;930:133-49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-39406-0_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27558820 Review.
Cited by
-
MnO2 Nanoflowers Induce Immunogenic Cell Death under Nutrient Deprivation: Enabling an Orchestrated Cancer Starvation-Immunotherapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020 Dec 31;8(4):2002667. doi: 10.1002/advs.202002667. eCollection 2021 Feb. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020. PMID: 33643794 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer and necroptosis: friend or foe?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Jun;73(11-12):2183-93. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2193-2. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27048810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Situ Tumor Vaccination with Nanoparticle Co-Delivering CpG and STAT3 siRNA to Effectively Induce Whole-Body Antitumor Immune Response.Adv Mater. 2021 Aug;33(31):e2100628. doi: 10.1002/adma.202100628. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Adv Mater. 2021. PMID: 34118167 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenic Human Papillomavirus Pseudovirus-Mediated Suicide-Gene Therapy for Bladder Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 14;17(7):1125. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071125. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27428950 Free PMC article.
-
Oncolytic Newcastle disease virus induces autophagy-dependent immunogenic cell death in lung cancer cells.Am J Cancer Res. 2018 Aug 1;8(8):1514-1527. eCollection 2018. Am J Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30210920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Obeid M, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Fimia GM, Apetoh L, Perfettini JL, et al. Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity of cancer cell death. Nat Med. 2007;13:54–61. - PubMed
-
- Thompson CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995;267:1456–1462. - PubMed
-
- Tanimoto T, Hori A, Kami M.Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer N Engl J Med 20103631967–1968.1966; author reply. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

