Polymorphism in tropomyosin structure and function
- PMID: 23832280
- PMCID: PMC4509547
- DOI: 10.1007/s10974-013-9353-x
Polymorphism in tropomyosin structure and function
Abstract
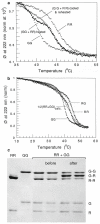
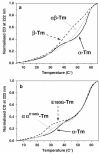
Tropomyosins (Tm) in humans are expressed from four distinct genes and by alternate splicing >40 different Tm polypeptide chains can be made. The functional Tm unit is a dimer of two parallel polypeptide chains and these can be assembled from identical (homodimer) or different (heterodimer) polypeptide chains provided both chains are of the same length. Since most cells express multiple isoforms of Tm, the number of different homo and heterodimers that can be assembled becomes very large. We review the mechanism of dimer assembly and how preferential assembly of some heterodimers is driven by thermodynamic stability. We examine how in vitro studies can reveal functional differences between Tm homo and heterodimers (stability, actin affinity, flexibility) and the implication for how there could be selection of Tm isomers in the assembly on to an actin filament. The role of Tm heterodimers becomes more complex when mutations in Tm are considered, such as those associated with cardiomyopathies, since mutations can appear in only one of the chains.
Figures

References
-
- Araya E, Berthier C, Kim E, Yeung T, Wang X, Helfman DM. Regulation of coiled-coil assembly in tropomyosins. J Struct Biol. 2002;137:176–183. doi:10.1006/jsbi.2002.4463. - PubMed
-
- Bicer S, Patel RJ, Williams JB, Reiser PJ. Patterns of tropomyosin and troponin-T isoform expression in jaw-closing muscles of mammals and reptiles that express masticatory myosin. J Exp Biol. 2011;214:1077–1085. doi:10.1242/jeb.049213. - PubMed
-
- Bicer S, Reiser PJ. Complex tropomyosin and troponin T isoform expression patterns in orbital and global fibers of adult dog and rat extraocular muscles. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2013 doi:10.1007/s10974-013-9346-9. - PubMed
-
- Bing W, Redwood CS, Purcell IF, Esposito G, Watkins H, Marston SB. Effects of two hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutations in alpha-tropomyosin, Asp175Asn and Glu180Gly, on Ca2+ regulation of thin filament motility. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;236:760–764. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.7045. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

