Osteoclast precursors in murine bone marrow express CD27 and are impeded in osteoclast development by CD70 on activated immune cells
- PMID: 23832783
- PMCID: PMC3725107
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1216082110
Osteoclast precursors in murine bone marrow express CD27 and are impeded in osteoclast development by CD70 on activated immune cells
Abstract
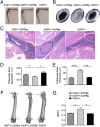
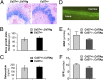
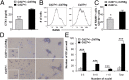
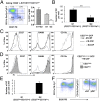
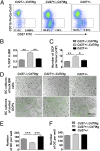
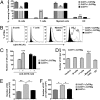
Osteoclasts (OCs) are bone-resorbing cells that are formed from hematopoietic precursors. OCs ordinarily maintain bone homeostasis, but they can also cause major pathology in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Under homeostatic conditions, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B (RANK) ligand on osteoblasts drives OC differentiation by interaction with its receptor RANK on OC precursors. During chronic immune activation, RANK ligand on activated immune cells likewise drives pathogenic OC differentiation. We here report that the related TNF family member CD70 and its receptor CD27 can also mediate cross-talk between immune cells and OC precursors. We identified CD27 on a rare population (0.3%) of B220(-)c-Kit(+)CD115(+)CD11b(low) cells in the mouse bone marrow (BM) that are highly enriched for osteoclastogenic potential. We dissected this population into CD27(high) common precursors of OC, dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages and CD27(low/neg) downstream precursors that could differentiate into OC and macrophages, but not DC. In a recombinant mouse model of chronic immune activation, sustained CD27/CD70 interactions caused an accumulation of OC precursors and a reduction in OC activity. These events were due to a CD27/CD70-dependent inhibition of OC differentiation from the OC precursors by BM-infiltrating, CD70(+)-activated immune cells. DC numbers in BM and spleen were increased, suggesting a skewing of the OC precursors toward DC differentiation. The impediment in OC differentiation culminated in a high trabecular bone mass pathology. Mice additionally presented anemia, leukopenia, and splenomegaly. Thus, under conditions of constitutive CD70 expression reflecting chronic immune activation, the CD27/CD70 system inhibits OC differentiation and favors DC differentiation.
Keywords: TNF receptor family; costimulation; hematopoiesis; osteoimmunology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic CD70-driven costimulation impairs IgG responses by instructing T cells to inhibit germinal center B cell formation through FasL-Fas interactions.J Immunol. 2009 Nov 15;183(10):6442-51. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901565. Epub 2009 Oct 28. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19864607
-
Epithelial and dendritic cells in the thymic medulla promote CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cell development via the CD27-CD70 pathway.J Exp Med. 2013 Apr 8;210(4):715-28. doi: 10.1084/jem.20112061. Epub 2013 Apr 1. J Exp Med. 2013. PMID: 23547099 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct osteoclast precursors in the bone marrow and extramedullary organs characterized by responsiveness to Toll-like receptor ligands and TNF-alpha.J Immunol. 2003 Nov 15;171(10):5130-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.10.5130. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14607912
-
Plasma cell generation from B-lymphocytes via CD27/CD70 interaction.Leuk Lymphoma. 1999 Oct;35(3-4):219-25. doi: 10.3109/10428199909145724. Leuk Lymphoma. 1999. PMID: 10706444 Review.
-
CD27/CD70 interactions regulate T dependent B cell differentiation.Immunol Res. 2000;21(1):23-30. doi: 10.1385/IR:21:1:23. Immunol Res. 2000. PMID: 10803880 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic role of PD-L1 and immune-related gene expression profiles in giant cell tumors of bone.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020 Sep;69(9):1905-1916. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02594-9. Epub 2020 May 6. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32377818 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling Pathway Mediates Inhalant Organic Dust-Induced Bone Loss.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 1;11(8):e0158735. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158735. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27479208 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Inhalant Organic Dust on Bone Health.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018 Feb 22;18(3):16. doi: 10.1007/s11882-018-0773-y. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018. PMID: 29470660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome profiling of osteoclast subsets associated with arthritis: A pathogenic role of CCR2hi osteoclast progenitors.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 15;13:994035. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.994035. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36591261 Free PMC article.
-
Knee and Hip Joint Cartilage Damage from Combined Spaceflight Hazards of Low-Dose Radiation Less than 1 Gy and Prolonged Hindlimb Unloading.Radiat Res. 2019 Jun;191(6):497-506. doi: 10.1667/RR15216.1. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Radiat Res. 2019. PMID: 30925135 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pittenger MF, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143–147. - PubMed
-
- Quinn JM, Elliott J, Gillespie MT, Martin TJ. A combination of osteoclast differentiation factor and macrophage-colony stimulating factor is sufficient for both human and mouse osteoclast formation in vitro. Endocrinology. 1998;139(10):4424–4427. - PubMed
-
- Lacey DL, et al. Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 1998;93(2):165–176. - PubMed
-
- Kong YY, et al. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature. 1999;397(6717):315–323. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

