Pancreatic and peripancreatic tuberculosis presenting as hypoechoic mass and malignancy diagnosed by ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology
- PMID: 23833404
- PMCID: PMC3701338
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-9371.112658
Pancreatic and peripancreatic tuberculosis presenting as hypoechoic mass and malignancy diagnosed by ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic and peripancreatic tuberculosis is an extremely uncommon disease, presenting as hypoechoic mass on ultrasonography and imaging mimicking malignancy. Consequently, it represents a diagnostic challenge.
Aims: To study 14 unusual cases of pancreatic and peripancreatic tuberculosis undergoing ultrasound-/endoscopic-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) in the 5-year period from 2006 to 2010.
Materials and methods: Endoscopic-guided FNAC was done in two cases, while ultrasound-guided FNAC was performed in 12 cases using 22-G needles via a percutaneous transabdominal approach. The aspirated material was quickly smeared onto glass slides, air dried, and wet fixed in 95% ethyl alcohol for subsequent Papanicolaou staining.
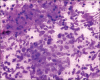
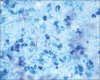
Results: All pancreatic and peripancreatic tuberculosis cases showed solid-cystic pancreatic mass. Smears showed epithelioid cell granulomas, multinucleated giant cells, mixed inflammatory cells and histiocytes against a necrotic background. The common anatomic locations were the head, peripancreatic, tail and body of the pancreas.
Conclusions: Ultrasound-/endoscopic-guided FNAC is a safe, reliable and cost-effective method for preoperative diagnosis of pancreatic and peripancreatic tuberculosis. Clinical symptoms and accurate diagnostic approach by ultrasound-/endoscopic-guided FNAC of pancreatic and peripancreatic tuberculosis is needed to avoid performing redundant laparotomy. Despite its rarity, pancreatic and peripancreatic tuberculosis should be considered for differential diagnosis of pancreatic and peripancreatic cystic mass in endemic developing countries.
Keywords: Cystic neoplasms; endoscopic; pancreas; pancreatitis; tuberculosis; ultrasound-FNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bhansali SK. Abdominal tuberculosis. Experiences with 300 cases. Am J Gastroenterol. 1977;67:324–37. - PubMed
-
- Woodfield JC, Windsor JA, Godfrey CC, Orr DA, Officer NM. Diagnosis and management of isolated pancreatic tuberculosis: Recent experience and literature review. ANZ J Surg. 2004;74:368–71. - PubMed
-
- Sanabe N, Ikematsu Y, Nishiwaki Y, Kida H, Murohisa G, Ozawa T, et al. Pancreatic tuberculosis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2002;9:515–8. - PubMed
-
- Ahlawat SK, Charabaty-Pishvaian A, Lewis JH, Haddad NG. Pancreatic tuberculosis diagnosed with endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration. JOP. 2005;6:598–602. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

