Role of transabdominal ultrasound of lung bases and follow-up in premature neonates with respiratory distress soon after birth
- PMID: 23833419
- PMCID: PMC3698890
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-3026.111480
Role of transabdominal ultrasound of lung bases and follow-up in premature neonates with respiratory distress soon after birth
Abstract
Background: Chest radiography has been the traditional method of diagnostic evaluation of patients of hyaline membrane disease (HMD). Lung sonography (USG) has been lately explored as an alternative modality.
Aims: To explore the application of transabdominal USG of lung bases (TASL) in the evaluation of HMD in premature neonates with respiratory distress soon after birth.
Settings and design: Tertiary care institutional setup. Study duration-18 months. Follow-up-variable, up to 1 month. Prospective descriptive study.
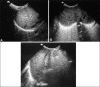
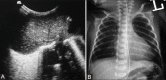
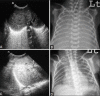
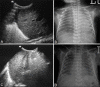
Materials and methods: Eighty-eight consecutive patients admitted in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) with gestational age <32 weeks having respiratory distress within 6 h of birth were enrolled. The diagnosis of HMD was made if the patient had negative gastric shake test and/or suggestive chest radiograph. TASL was performed in all patients within the first 24 h of life and biweekly subsequently. USG was interpreted as normal, HMD pattern, or broncho-pulmonary dysplasia (BPD) pattern. Biweekly follow-up was done for patients showing HMD till normalization of the sonographic HMD pattern, development of the sonographic BPD pattern, or death/discharge of the neonate from the hospital.
Results and conclusions: TASL showed 85.7% sensitivity, 75% specificity, 88.88% positive predictive value, and 69.2% negative predictive value for the diagnosis of HMD. The abnormal sonographic findings on day 14 had 94.1% accuracy for prediction of eventual occurrence of clinical BPD. TASL is complementary to chest radiograph in the diagnosis of HMD. It is also useful for the early prediction of BPD with the potential of reducing the cumulative radiation dose to these neonates.
Keywords: Hyperechogenicity; neonates; respiratory distress syndrome; transabdominal; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic value of gastric shake test for hyaline membrane disease in preterm infant.Iran J Reprod Med. 2014 Jul;12(7):487-91. Iran J Reprod Med. 2014. PMID: 25114671 Free PMC article.
-
The value of ultrasound examination of the lungs in predicting bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Pediatr Radiol. 2004 Mar;34(3):227-31. doi: 10.1007/s00247-003-1102-7. Epub 2003 Dec 17. Pediatr Radiol. 2004. PMID: 14685792
-
Hyaline membrane disease in the newborn: diagnosis by ultrasound.Pediatr Radiol. 1990;20(3):143-6. doi: 10.1007/BF02012957. Pediatr Radiol. 1990. PMID: 2191263
-
Inhalation or instillation of steroids for the prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia.Neonatology. 2015;107(4):358-9. doi: 10.1159/000381132. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Neonatology. 2015. PMID: 26044104 Review.
-
From the archives of the AFIP: Lung disease in premature neonates: radiologic-pathologic correlation.Radiographics. 2005 Jul-Aug;25(4):1047-73. doi: 10.1148/rg.254055019. Radiographics. 2005. PMID: 16009823 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Performance of Point of Care Ultrasonography in Identifying the Etiology of Respiratory Distress in Neonates.Indian J Pediatr. 2017 Apr;84(4):267-270. doi: 10.1007/s12098-016-2288-7. Epub 2017 Jan 21. Indian J Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28108881
-
ChatGPT: Chasing the Storm in Radiology Training and Education.Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2023 Oct 5;33(4):431-435. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1774743. eCollection 2023 Oct. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37811181 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Lung ultrasound (LUS) in pre-term neonates with respiratory distress: A prospective observational study.Lung India. 2022 Sep-Oct;39(5):417-421. doi: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_13_22. Lung India. 2022. PMID: 36629201 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound Lung Image under Artificial Intelligence Algorithm in Diagnosis of Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Mar 27;2022:1817341. doi: 10.1155/2022/1817341. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9853713. doi: 10.1155/2023/9853713. PMID: 35387221 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Chest and lung ultrasound in childhood: applications, role, value and limitations.J Ultrason. 2018;18(75):281-283. doi: 10.15557/JoU.2018.0040. J Ultrason. 2018. PMID: 30763010 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kinsella JP, Greenough A, Abman SH. BPD. Lancet. 2006;367:1421–31. - PubMed
-
- Guyer B, Hoyert DL, Martin JA, Ventura SJ, MacDorman MF, Strobino DM. Annual summary of vital statistics--1998. Pediatrics. 1999;104:1229–46. - PubMed
-
- Jobe AH, Bancalari E. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163:1723–9. - PubMed
-
- Toce SS, Farrell PM, Leavitt LA, Samuels DP, Edwards DK. Clinical and roentgenographic scoring systems for assessing BPD. Am J Dis Child. 1984;138:581–5. - PubMed
-
- Maconochie I, Greenough A, Yuksel B, Page A, Karani J. A chest radiograph scoring system to predict chronic oxygen dependency in low birth weight infants. Early Hum Dev. 1991;26:37–43. - PubMed

