Aberrant expression of the PHF14 gene in biliary tract cancer cells
- PMID: 23833654
- PMCID: PMC3700892
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2013.1278
Aberrant expression of the PHF14 gene in biliary tract cancer cells
Abstract
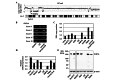
DNA copy number aberrations in human biliary tract cancer (BTC) cell lines were investigated using a high-density oligonucleotide microarray. A novel homozygous deletion was detected at chromosomal region 7p21.3 in the OZ cell line. Further validation experiments using genomic PCR revealed a homozygous deletion of a single gene, plant homeodomain (PHD) finger protein 14 (PHF14). No PHF14 mRNA or protein expression was detected, thus demonstrating the absence of PHF14 expression in the OZ cell line. Although the PHD finger protein is considered to be involved in chromatin-mediated transcriptional regulation, little is known about the function of PHF14 in cancer. The present study observed that the knock down of PHF14 using small interfering RNA (siRNA) enhanced the growth of the BTC cells. These observations suggest that aberrant PHF14 expression may have a role in the tumorigenesis of BTC.
Keywords: PHF14; biliary tract cancer; deletion.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Silencing expression of PHF14 in glioblastoma promotes apoptosis, mitigates proliferation and invasiveness via Wnt signal pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Nov 27;19:314. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-1040-6. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 31798343 Free PMC article.
-
A novel PHD-finger protein 14/KIF4A complex overexpressed in lung cancer is involved in cell mitosis regulation and tumorigenesis.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 21;8(12):19684-19698. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14962. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28160558 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of PHF14, a novel histone-binding protein gene, causes neonatal lethality in mice due to respiratory failure.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2013 Aug;45(8):622-33. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmt055. Epub 2013 May 20. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2013. PMID: 23688586
-
A comprehensive pan-cancer analysis unveiling the oncogenic effect of plant homeodomain finger protein 14 (PHF14) in human tumors.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 10;14:1073138. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1073138. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37007943 Free PMC article.
-
PHF14 knockdown causes apoptosis by inducing DNA damage and impairing the activity of the damage response complex in colorectal cancer.Cancer Lett. 2022 Apr 10;531:109-123. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.01.002. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 35074497
Cited by
-
Integrative genomic and transcriptomic analysis identified candidate genes implicated in the pathogenesis of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 24;9(7):e102977. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102977. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25057852 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing expression of PHF14 in glioblastoma promotes apoptosis, mitigates proliferation and invasiveness via Wnt signal pathway.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 Nov 27;19:314. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-1040-6. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 31798343 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Exome Sequencing Identifies PHF14 Mutations in Neurocytoma and Predicts Responsivity to the PDGFR Inhibitor Sunitinib.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 8;10(11):2842. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112842. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36359362 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide detection of copy number variation using SNP genotyping arrays in Beijing-You chickens.Genetica. 2014 Oct;142(5):441-50. doi: 10.1007/s10709-014-9788-z. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Genetica. 2014. PMID: 25214021
-
Molecular basis for bipartite recognition of histone H3 by the PZP domain of PHF14.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Sep 7;49(15):8961-8973. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab670. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34365506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Koti RS, Davidson BR. Malignant biliary diseases. In: Dooley JS, Lok ASF, Burroughs AK, Heathcote EJ, editors. Sherlock’s Diseases of the Liver and Biliary System. 12th edition. Wiley-Blackwell; Oxford: 2011. pp. 294–311.
-
- Goodman ZD, Terracciano LM, Wee A. Tumours and tumour-like lesions of the liver. In: Burt A, Portmann B, Ferrell L, editors. MacSween’s Pathology of the Liver. 6th edition. Churchill Livingstone; Philadelphia: 2011. pp. 761–851.
-
- Zen K, Yasui K, Gen Y, et al. Defective expression of polarity protein PAR-3 gene (PARD3) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2009;28:2910–2918. - PubMed
-
- Endo M, Yasui K, Zen Y, et al. Alterations of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling subunit-BRG1 and BRM in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2013;33:105–117. - PubMed
-
- Zen K, Yasui K, Nakajima T, et al. ERK5 is a target for gene amplification at 17p11 and promotes cell growth in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating mitotic entry. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2009;48:109–120. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
