Aqueous extract of Saussurea lappa root ameliorate oxidative myocardial injury induced by isoproterenol in rats
- PMID: 23833749
- PMCID: PMC3696228
- DOI: 10.4103/2231-4040.111525
Aqueous extract of Saussurea lappa root ameliorate oxidative myocardial injury induced by isoproterenol in rats
Abstract
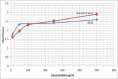
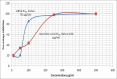
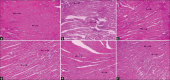
Saussurea lappa Clarke (Compositae), is commonly known as Kushta. In Ayurvedha, it is mentioned that the aqueous extract of the root S. lappa was used for treatment of angina pectoris. The present study was designed to investigate the cardioprotective effect of aqueous extract of root of S. lappa against isoproterenol induced myocardial injury. Myocardial injury in rat was induced by the administration of isoproterenol at a dose of 85 mg/kg, i.p., The rats were pretreated with the aqueous extract of S. lappa (AESL) in three different doses (100, 200 and 300 mg/kg, p.o.) through the oral route. Isoproterenol alone-treated rats showed increased serum concentration of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatinine kinase (CK), and aspartate transaminase (AST), increased myocardial thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) level, and decreased myocardial glutathione (GSH) level due to myocardial damage produced by isoproterenol. This is further conformed by histopathological changes. Chronic oral administration of AESL in three different doses significantly restored the level of myocardial LDH, CK, AST, TBARS, and GSH. The extract effect was compared with the reference standard α-tocopherol which also offered similar protection in biochemical and histopathological changes. The overall beneficial effect which was observed with the dose of 200 mg/kg indicated that AESL produced significant dose-dependent activity against isoproterenol induced myocardial injury.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Saussurea lappa; lactate dehydrogenase; myocardial infarction; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kumar A, Khan SA, Parvez A, Zaheer MS, Rabbani MU, Zafar L. The prevalence of hyperhomocysteinemia and its correlation with conventional risk factors in young patients with myocardial infarction in a tertiary care centre of India. Biomed Res. 2011;22:225–9.
-
- Saleem TS, Chetty M, Kavimani S. Sesame oil enhances endogenous antioxidants in ischemic myocardium of rat. Rev Bras Farmacogn. 2012;22:669–75.
-
- Ahmad S, Khan MB, Hoda MN, Bhatia K, Haque R, Fazili IS, et al. Neuroprotective effect of sesame seed oil in 6-hydroxydopamine induced neurotoxicity in mice model: Cellular, biochemical and neurochemical evidence. Neurochem Res. 2012;37:516–26. - PubMed
-
- Shah NC. Herbal folk medicines in Northern India. J Ethnopharmacol. 1982;6:293–301. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
