A genomic update on clostridial phylogeny: Gram-negative spore formers and other misplaced clostridia
- PMID: 23834245
- PMCID: PMC4056668
- DOI: 10.1111/1462-2920.12173
A genomic update on clostridial phylogeny: Gram-negative spore formers and other misplaced clostridia
Abstract
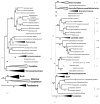
The class Clostridia in the phylum Firmicutes (formerly low-G+C Gram-positive bacteria) includes diverse bacteria of medical, environmental and biotechnological importance. The Selenomonas-Megasphaera-Sporomusa branch, which unifies members of the Firmicutes with Gram-negative-type cell envelopes, was recently moved from Clostridia to a separate class Negativicutes. However, draft genome sequences of the spore-forming members of the Negativicutes revealed typically clostridial sets of sporulation genes. To address this and other questions in clostridial phylogeny, we have compared a phylogenetic tree for a concatenated set of 50 widespread ribosomal proteins with the trees for beta subunits of the RNA polymerase (RpoB) and DNA gyrase (GyrB) and with the 16S rRNA-based phylogeny. The results obtained by these methods showed remarkable consistency, suggesting that they reflect the true evolutionary history of these bacteria. These data put the Selenomonas-Megasphaera-Sporomusa group back within the Clostridia. They also support placement of Clostridium difficile and its close relatives within the family Peptostreptococcaceae; we suggest resolving the long-standing naming conundrum by renaming it Peptoclostridium difficile. These data also indicate the existence of a group of cellulolytic clostridia that belong to the family Ruminococcaceae. As a tentative solution to resolve the current taxonomical problems, we propose assigning 78 validly described Clostridium species that clearly fall outside the family Clostridiaceae to six new genera: Peptoclostridium, Lachnoclostridium, Ruminiclostridium, Erysipelatoclostridium, Gottschalkia and Tyzzerella. This work reaffirms that 16S rRNA and ribosomal protein sequences are better indicators of evolutionary proximity than phenotypic traits, even such key ones as the structure of the cell envelope and Gram-staining pattern.
Published 2013. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures
References
-
- Beuscher HU, Andreesen JR. Eubacterium angustum sp. nov., a Gram-positive anaerobic, non-sporeforming, obligate purine fermenting organism. Arch Microbiol. 1984;140:2–8.
-
- Cai S, Dong X. Cellulosilyticum ruminicola gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the rumen of yak, and reclassification of Clostridium lentocellum as Cellulosilyticum lentocellum comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2010;60:845–849. - PubMed
-
- Carlier JP, Bedora-Faure M, K’Ouas G, Alauzet C, Mory F. Proposal to unify Clostridium orbiscindens Winter et al. 1991 and Eubacterium plautii (Seguin 1928) Hofstad and Aasjord 1982, with description of Flavonifractor plautii gen. nov., comb. nov., and reassignment of Bacteroides capillosus to Pseudoflavonifractor capillosus gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2010;60:585–590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

