Transplant tolerance to pancreatic islets is initiated in the graft and sustained in the spleen
- PMID: 23834659
- PMCID: PMC3869180
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.12333
Transplant tolerance to pancreatic islets is initiated in the graft and sustained in the spleen
Abstract
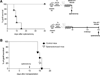
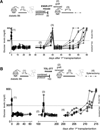
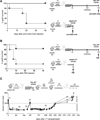
The immune system is comprised of several CD4(+) T regulatory (Treg) cell types, of which two, the Foxp3(+) Treg and T regulatory type 1 (Tr1) cells, have frequently been associated with transplant tolerance. However, whether and how these two Treg-cell types synergize to promote allograft tolerance remains unknown. We previously developed a mouse model of allogeneic transplantation in which a specific immunomodulatory treatment leads to transplant tolerance through both Foxp3(+) Treg and Tr1 cells. Here, we show that Foxp3(+) Treg cells exert their regulatory function within the allograft and initiate engraftment locally and in a non-antigen (Ag) specific manner. Whereas CD4(+) CD25(-) T cells, which contain Tr1 cells, act from the spleen and are key to the maintenance of long-term tolerance. Importantly, the role of Foxp3(+) Treg and Tr1 cells is not redundant once they are simultaneously expanded/induced in the same host. Moreover, our data show that long-term tolerance induced by Foxp3(+) Treg-cell transfer is sustained by splenic Tr1 cells and functionally moves from the allograft to the spleen.
Keywords: Graft; T regulatory cells; spleen; transplant tolerance.
© Copyright 2013 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure
The authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the
Figures




Comment in
-
An orchestrated dance between differing regulatory T cell phenotypes in allograft tolerance.Am J Transplant. 2013 Aug;13(8):1945-6. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12336. Am J Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23890281 No abstract available.
References
-
- Littman DR, Rudensky AY. Th17 and regulatory T cells in mediating and restraining inflammation. Cell. 2010;140(6):845–858. - PubMed
-
- Li XC, Turka LA. An update on regulatory T cells in transplant tolerance and rejection. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010;6(10):577–583. - PubMed
-
- Feuerer M, Hill JA, Mathis D, et al. Foxp3+ regulatory T cells: Differentiation, specification, subphenotypes. Nat Immunol. 2009;10(7):689–695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

