The role of interleukin 17 in Crohn's disease-associated intestinal fibrosis
- PMID: 23834907
- PMCID: PMC3733737
- DOI: 10.1186/1755-1536-6-13
The role of interleukin 17 in Crohn's disease-associated intestinal fibrosis
Abstract
Background: Interleukin (IL)-17A and IL-17E (also known as IL-25) have been implicated in fibrosis in various tissues. However, the role of these cytokines in the development of intestinal strictures in Crohn's disease (CD) has not been explored. We investigated the levels of IL-17A and IL-17E and their receptors in CD strictured and non-strictured gut, and the effects of IL-17A and IL-17E on CD myofibroblasts.
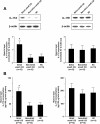
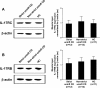
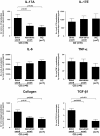
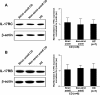
Results: IL-17A was significantly overexpressed in strictured compared with non-strictured CD tissues, whereas no significant difference was found in the expression of IL-17E or IL-17A and IL-17E receptors (IL-17RC and IL-17RB, respectively) in strictured and non-strictured CD areas. Strictured CD explants released significantly higher amounts of IL-17A than non-strictured explants, whereas no difference was found as for IL-17E, IL-6, or tumor necrosis factor-α production. IL-17A, but not IL-17E, significantly inhibited myofibroblast migration, and also significantly upregulated matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3, MMP-12, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and collagen production by myofibroblasts from strictured CD tissues.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that IL-17A, but not IL-17E, is pro-fibrotic in CD. Further studies are needed to clarify whether the therapeutic blockade of IL-17A through the anti-IL-17A monoclonal antibody secukinumab is able to counteract the fibrogenic process in CD.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transforming growth factor beta signalling and matrix metalloproteinases in the mucosa overlying Crohn's disease strictures.Gut. 2009 Jun;58(6):777-89. doi: 10.1136/gut.2008.149096. Epub 2009 Feb 6. Gut. 2009. PMID: 19201776
-
Involvement of interleukin-17A-induced expression of heat shock protein 47 in intestinal fibrosis in Crohn's disease.Gut. 2014 Dec;63(12):1902-12. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2013-305632. Epub 2014 Feb 17. Gut. 2014. PMID: 24534724
-
Inhibition of Fibroblast Activation Protein Restores a Balanced Extracellular Matrix and Reduces Fibrosis in Crohn's Disease Strictures Ex Vivo.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018 Jan 18;24(2):332-345. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izx008. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018. PMID: 29361086
-
Mechanism of fibrosis and stricture formation in Crohn's disease.Scand J Immunol. 2020 Dec;92(6):e12990. doi: 10.1111/sji.12990. Scand J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33119150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-17 family cytokines in protective immunity against infections: role of hematopoietic cell-derived and non-hematopoietic cell-derived interleukin-17s.Microbiol Immunol. 2018 Jan;62(1):1-13. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12560. Microbiol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29205464 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Certain Interleukins as Novel Treatment Options for Liver Fibrosis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 24;12:645703. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.645703. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33841164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Oxysterol Synthesising Enzyme CH25H Contributes to the Development of Intestinal Fibrosis.J Crohns Colitis. 2019 Sep 19;13(9):1186-1200. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjz039. J Crohns Colitis. 2019. PMID: 31220227 Free PMC article.
-
Medical Therapy of Fibrostenotic Crohn's Disease.Viszeralmedizin. 2015 Aug;31(4):259-64. doi: 10.1159/000435868. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Viszeralmedizin. 2015. PMID: 26557834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine and anti-cytokine therapies in prevention or treatment of fibrosis in IBD.United European Gastroenterol J. 2016 Aug;4(4):531-40. doi: 10.1177/2050640616649356. Epub 2016 May 10. United European Gastroenterol J. 2016. PMID: 27536363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-17: Friend or foe in organ fibrosis.Cytokine. 2019 Aug;120:282-288. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.11.003. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 30772195 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Valente AJ, Yoshida T, Gardner JD, Somanna N, Delafontaine P, Chandrasekar B. Interleukin-17A stimulates cardiac fibroblast proliferation and migration via negative regulation of the dual-specificity phosphatase MKP-1/DUSP-1. Cell Signal. 2012;24:560–568. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.10.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

