Evaluation of hybrid inverse planning and optimization (HIPO) algorithm for optimization in real-time, high-dose-rate (HDR) brachytherapy for prostate
- PMID: 23835384
- PMCID: PMC5714541
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v14i4.4198
Evaluation of hybrid inverse planning and optimization (HIPO) algorithm for optimization in real-time, high-dose-rate (HDR) brachytherapy for prostate
Abstract
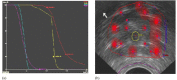
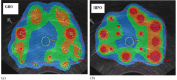
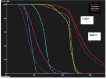
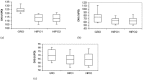
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effectiveness of the HIPO planning and optimization algorithm for real-time prostate HDR brachytherapy. This study consists of 20 patients who underwent ultrasound-based real-time HDR brachytherapy of the prostate using the treatment planning system called Oncentra Prostate (SWIFT version 3.0). The treatment plans for all patients were optimized using inverse dose-volume histogram-based optimization followed by graphical optimization (GRO) in real time. The GRO is manual manipulation of isodose lines slice by slice. The quality of the plan heavily depends on planner expertise and experience. The data for all patients were retrieved later, and treatment plans were created and optimized using HIPO algorithm with the same set of dose constraints, number of catheters, and set of contours as in the real-time optimization algorithm. The HIPO algorithm is a hybrid because it combines both stochastic and deterministic algorithms. The stochastic algorithm, called simulated annealing, searches the optimal catheter distributions for a given set of dose objectives. The deterministic algorithm, called dose-volume histogram-based optimization (DVHO), optimizes three-dimensional dose distribution quickly by moving straight downhill once it is in the advantageous region of the search space given by the stochastic algorithm. The PTV receiving 100% of the prescription dose (V100) was 97.56% and 95.38% with GRO and HIPO, respectively. The mean dose (D(mean)) and minimum dose to 10% volume (D10) for the urethra, rectum, and bladder were all statistically lower with HIPO compared to GRO using the student pair t-test at 5% significance level. HIPO can provide treatment plans with comparable target coverage to that of GRO with a reduction in dose to the critical structures.
Figures





References
-
- Lachance B, Béliveau‐Nadeau D, Lessard E et al. Early clinical experience with anatomy‐based inverse planning dose optimization for high‐dose‐rate boost of the prostate. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;54(1):86–100. - PubMed
-
- Demanes DJ, Rodriguez RR, Schour L, Brandt D, Altieri G. High‐dose‐rate intensity‐modulated brachytherapy with external beam radiotherapy for prostate cancer: California endocurietherapy's 10‐year results. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61(5):1306–16. - PubMed
-
- Tang JI, Williams SG, Tai KH, Dean J, Duchesue GM. A prospective dose escalation trial of high‐dose‐rate brachytherapy boost for prostate cancer: evidence of hypofractionation efficacy? Brachytherapy. 2006;5(4):256–61. - PubMed
-
- Lessard E and Pouliot J. Inverse planning anatomy‐based dose optimization for HDR‐brachytherapy of the prostate using fast simulated annealing algorithm and dedicated objective function. Med Phys. 2001;28(5):773–79. - PubMed
-
- Lahans M. Anatomy‐based three‐dimensional dose optimization in brachytherapy using multiobjective genetic algorithms. Med Phys. 1999;26(9):1904–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

