EGFR gets in the way of microRNA biogenesis
- PMID: 23835474
- PMCID: PMC3790241
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2013.87
EGFR gets in the way of microRNA biogenesis
Abstract
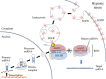
Recent studies suggest that microRNA (miRNA) processing is a key regulatory step in the miRNA biogenesis as well as its transcriptional control. In a paper recently published in Nature, Shen et al. revealed that epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) directly interacts with argonaute 2 (AGO2), a critical component of RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), and inhibits the maturation of specific tumor suppressive miRNAs under hypoxic condition.
Figures
Comment on
-
EGFR modulates microRNA maturation in response to hypoxia through phosphorylation of AGO2.Nature. 2013 May 16;497(7449):383-7. doi: 10.1038/nature12080. Epub 2013 May 1. Nature. 2013. PMID: 23636329 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

