Understanding the hepatitis C virus life cycle paves the way for highly effective therapies
- PMID: 23836234
- PMCID: PMC3984536
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3248
Understanding the hepatitis C virus life cycle paves the way for highly effective therapies
Abstract
More than two decades of intense research has provided a detailed understanding of hepatitis C virus (HCV), which chronically infects 2% of the world's population. This effort has paved the way for the development of antiviral compounds to spare patients from life-threatening liver disease. An exciting new era in HCV therapy dawned with the recent approval of two viral protease inhibitors, used in combination with pegylated interferon-α and ribavirin; however, this is just the beginning. Multiple classes of antivirals with distinct targets promise highly efficient combinations, and interferon-free regimens with short treatment duration and fewer side effects are the future of HCV therapy. Ongoing and future trials will determine the best antiviral combinations and whether the current seemingly rich pipeline is sufficient for successful treatment of all patients in the face of major challenges, such as HCV diversity, viral resistance, the influence of host genetics, advanced liver disease and other co-morbidities.
Figures

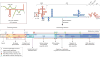

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI072613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI091707/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI090055/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI075099/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI090055/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI075099/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI072613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK085713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI099284/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI099284/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI091707/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA057973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK085713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA057973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

