Neutralizing nanobodies targeting diverse chemokines effectively inhibit chemokine function
- PMID: 23836909
- PMCID: PMC3757181
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.467969
Neutralizing nanobodies targeting diverse chemokines effectively inhibit chemokine function
Abstract
Chemokine receptors and their ligands play a prominent role in immune regulation but many have also been implicated in inflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, allograft rejection after transplantation, and also in cancer metastasis. Most approaches to therapeutically target the chemokine system involve targeting of chemokine receptors with low molecular weight antagonists. Here we describe the selection and characterization of an unprecedented large and diverse panel of neutralizing Nanobodies (single domain camelid antibodies fragment) directed against several chemokines. We show that the Nanobodies directed against CCL2 (MCP-1), CCL5 (RANTES), CXCL11 (I-TAC), and CXCL12 (SDF-1α) bind the chemokines with high affinity (at nanomolar concentration), thereby blocking receptor binding, inhibiting chemokine-induced receptor activation as well as chemotaxis. Together, we show that neutralizing Nanobodies can be selected efficiently for effective and specific therapeutic treatment against a wide range of immune and inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Antibodies; Chemokines; Chemotaxis; G Protein-coupled Receptors (GPCR); Nanobodies; Radioreceptor Assays.
Figures

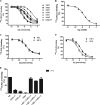
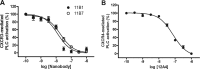

References
-
- Murphy P. M., Baggiolini M., Charo I. F., Hébert C. A., Horuk R., Matsushima K., Miller L. H., Oppenheim J. J., Power C. A. (2000) International union of pharmacology. XXII. Nomenclature for chemokine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 52, 145–176 - PubMed
-
- Comerford I., Nibbs R. J. (2005) Post-translational control of chemokines. A role for decoy receptors? Immunology Letters 96, 163–174 - PubMed
-
- Allen S. J., Crown S. E., Handel T. M. (2007) Chemokine. Receptor structure, interactions, and antagonism. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25, 787–820 - PubMed
-
- Trinker M., Kungl A. (2012) Targeting chemokine-glycan interactions. The CellJammer® technology platform. Drug Discovery Today Technol. 9, e253-e259 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

