Arrival time parametric imaging using Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography is useful for the detection of spoke-wheel patterns of focal nodular hyperplasia smaller than 3 cm
- PMID: 23837029
- PMCID: PMC3702692
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2013.1048
Arrival time parametric imaging using Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography is useful for the detection of spoke-wheel patterns of focal nodular hyperplasia smaller than 3 cm
Abstract
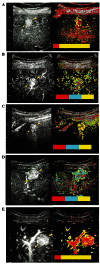
It is considered difficult to make a definitive diagnosis of focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) of <3 cm when using conventional diagnostic imaging modalities. Typical FNH imaging findings are: i) central scar formation, ii) nutrient vessels extending radially from the center and iii) the presence of Kupffer cells. In a clinical setting, identification of a spoke-wheel pattern formed by nutrient vessels extending radially is a key feature in the diagnosis of FNH. In this study, we investigated the detection rate of spoke-wheel patterns of FNH <3 cm using arrival time parametric imaging (At-PI) technology with Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography (US). Five patients with FNH <3 cm who had undergone Sonazoid-enhanced US at the Toho University Omori Medical Center between February 2008 and March 2009 were included in the study. The mean tumor diameter was 20.2±7.2 mm. Lesions were enhanced with 0.5 ml Sonazoid US contrast agent and a video of the procedure was saved and used for At-PI analysis of contrast agent dynamics in FNH. Three ultrasonographic specialists examined the images and made a diagnosis of FNH based on the findings of spoke-wheel patterns. Similarly, micro-flow imaging (MFI) was performed to evaluate the contrast agent dynamics in FNH. Using MFI, FNH was diagnosed in 3 of the 5 cases by the three specialists, whereas At-PI enabled the identification of spoke-wheel patterns in all 5 cases. At-PI using Sonazoid-enhanced US is superior for detecting spoke-wheel patterns of FNH <3 cm.
Keywords: Sonazoid; arrival time parametric imaging; contrast-enhanced ultrasonography; focal nodular hyperplasia; micro-flow imaging; spoke-wheel pattern.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of Super-Resolution US and Contrast Material-enhanced US in Detection of the Spoke Wheel Sign in Patients with Focal Nodular Hyperplasia.Radiology. 2021 Jan;298(1):82-90. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020200885. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Radiology. 2021. PMID: 33107798
-
Comparison Between SonoVue and Sonazoid Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in Characterization of Focal Nodular Hyperplasia Smaller Than 3 cm.J Ultrasound Med. 2021 Oct;40(10):2095-2104. doi: 10.1002/jum.15589. Epub 2020 Dec 11. J Ultrasound Med. 2021. PMID: 33305869
-
Focal nodular hyperplasia: spoke-wheel arterial pattern and other signs on dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasonography.Eur J Radiol. 2007 Aug;63(2):290-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.01.026. Epub 2007 Mar 13. Eur J Radiol. 2007. PMID: 17353110
-
Imaging modalities for focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatocellular adenoma.Dig Surg. 2010;27(1):46-55. doi: 10.1159/000268407. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Dig Surg. 2010. PMID: 20357451 Review.
-
Focal nodular hyperplasia: findings at state-of-the-art MR imaging, US, CT, and pathologic analysis.Radiographics. 2004 Jan-Feb;24(1):3-17; discussion 18-9. doi: 10.1148/rg.241035050. Radiographics. 2004. PMID: 14730031 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of parametric imaging on contrast-enhanced ultrasound of breast cancer.J Med Ultrason (2001). 2016 Apr;43(2):227-35. doi: 10.1007/s10396-015-0692-7. Epub 2016 Jan 22. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2016. PMID: 26801662
-
Assessment of renal perfusion impairment in a rat model of acute renal congestion using contrast-enhanced ultrasonography.Heart Vessels. 2018 Apr;33(4):434-440. doi: 10.1007/s00380-017-1063-7. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Heart Vessels. 2018. PMID: 29027577
-
Arrival-Time Parametric Imaging in Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound for Thyroid Nodule Differentiation.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Dec 27;30:e945793. doi: 10.12659/MSM.945793. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 39726208 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Diagnostic Imaging: Arrival-Time Parametric Imaging in Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound for Multi-Organ Assessment.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Nov 28;30:e945281. doi: 10.12659/MSM.945281. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 39604210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differentiation of atypical hepatic hemangioma from liver metastases: Diagnostic performance of a novel type of color contrast enhanced ultrasound.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Mar 7;26(9):960-972. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i9.960. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32206006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ueda K, Matsui O, Kawamori Y, et al. Differentiation of hyper-vascular hepatic pseudolesions from hepatocellular carcinoma: value of single-level dynamic CT during hepatic arteriography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1998;22:703–708. - PubMed
-
- Brancatelli G, Federle MP, Grazioli L, Blachar A, Peterson MS, Thaete L. Focal nodular hyperplasia: CT findings with emphasis on multiphasic helical CT in 78 patients. Radiology. 2001;219:61–68. - PubMed
-
- Ungermann L, Eliás P, Zizka J, Ryska P, Klzo L. Focal nodular hyperplasia: spoke-wheel arterial pattern and other signs on dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. Eur J Radiol. 2007;63:290–294. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi M, Maruyama H, Ishibashi H, Yoshikawa M, Yokosuka O. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound with perflubutane microbubble agent: evaluation of differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196:W123–W131. - PubMed
-
- Hiraoka A, Hirooka M, Koizumi Y, et al. Modified technique for determining therapeutic response to radiofrequency ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma using US-volume system. Oncol Rep. 2010;23:493–497. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
