Steroids as external temporal codes act via microRNAs and cooperate with cytokines in differential neurogenesis
- PMID: 23839338
- PMCID: PMC4049850
- DOI: 10.4161/fly.25241
Steroids as external temporal codes act via microRNAs and cooperate with cytokines in differential neurogenesis
Abstract
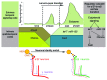
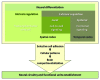
The generation of neuronal cell diversity is controlled by interdependent mechanisms, including cell intrinsic programs and environmental cues. During development, the astonishing variety of neurons is originated according to a precise timetable that is managed by a complex network of genes specifying individual types of neurons. Different neurons express specific sets of transcription factors, and they can be recognized by morphological characteristics and spatial localization, but, most importantly, they connect to each other and form functional units in a stereotyped fashion. This connectivity depends, mostly, on selective cell adhesion that is strictly regulated. While intrinsic factors specifying neuronal temporal identity have been extensively studied, an extrinsic temporal factor controlling neuronal temporal identity switch has not been shown. Our data demonstrate that pulses of steroid hormone act as a temporal cue to fine-tune neuronal cell differentiation. Here we also provide evidence that extrinsic JAK/STAT cytokine signaling acts as a spatial code in the process. Particularly, in Drosophila mushroom bodies, neuronal identity transition is controlled by steroid-dependent microRNAs that regulate spatially distributed cytokine-dependent signaling factors that in turn modulate cell adhesion. A new era of neuronal plasticity assessment via managing external temporal cues such as hormones and cytokines that specify individual types of neurons might open new possibilities for brain regenerative therapeutics.
Keywords: Drosophila mushroom body; JAK/STAT cytokine signaling; differential cell adhesion; microRNA let-7; steroid hormone ecdysone; temporal identity switch.
Figures

Comment on
-
Steroid-induced microRNA let-7 acts as a spatio-temporal code for neuronal cell fate in the developing Drosophila brain.EMBO J. 2012 Dec 12;31(24):4511-23. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.298. Epub 2012 Nov 16. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 23160410 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
