Long-term impact on healthcare resource utilization of statin treatment, and its cost effectiveness in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a record linkage study
- PMID: 23839541
- PMCID: PMC3909301
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht232
Long-term impact on healthcare resource utilization of statin treatment, and its cost effectiveness in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a record linkage study
Abstract
Aims: To assess the impact on healthcare resource utilization, costs, and quality of life over 15 years from 5 years of statin use in men without a history of myocardial infarction in the West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study (WOSCOPS).
Methods: Six thousand five hundred and ninety-five participants aged 45-54 years were randomized to 5 years treatment with pravastatin (40 mg) or placebo. Linkage to routinely collected health records extended follow-up for secondary healthcare resource utilization to 15 years. The following new results are reported: cause-specific first and recurrent cardiovascular hospital admissions including myocardial infarction, heart failure, stroke, coronary revascularization and angiography; non-cardiovascular hospitalization; days in hospital; quality-adjusted life years (QALYs); costs of pravastatin treatment, treatment safety monitoring, and hospital admissions.
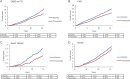
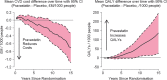
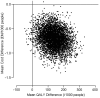
Results: Five years treatment of 1000 patients with pravastatin (40 mg/day) saved the NHS £710 000 (P < 0.001), including the cost of pravastatin and lipid and safety monitoring, and gained 136 QALYs (P = 0.017) over the 15-year period. Benefits per 1000 subjects, attributable to prevention of cardiovascular events, included 163 fewer admissions and a saving of 1836 days in hospital, with fewer admissions for myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure and coronary revascularization. There was no excess in non-cardiovascular admissions or costs (or in admissions associated with diabetes or its complications) and no evidence of heterogeneity of effect over sub-groups defined by baseline cardiovascular risk.
Conclusion: Five years' primary prevention treatment of middle-aged men with a statin significantly reduces healthcare resource utilization, is cost saving, and increases QALYs. Treatment of even younger, lower risk individuals is likely to be cost-effective.
Keywords: Cardiovascular outcomes; Cost effectiveness; Pravastatin; Primary prevention; Record linkage.
Figures
References
-
- West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study Group. A coronary primary prevention study of Scottish men aged 45–64 years: trial design. J Clin Epidemiol. 1992;45:849–860. - PubMed
-
- The WOSCOPS Study Group. Screening experience and baseline characteristics in the West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study. Am J Cardiol. 1995;76:485–491. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd J, Cobbe SM, Ford I, Isles CG, Lorimer AR, Macfarlane PW, McKillop JH, Packard CJ. Prevention of coronary heart disease with pravastatin in men with hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1301–1307. - PubMed
-
- Ford I, Murray H, Packard CJ, Shepherd J, Macfarlane P, Cobbe SM. Long-term follow-up of the West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1477–1486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

