Influence of gut microbiota on subclinical inflammation and insulin resistance
- PMID: 23840101
- PMCID: PMC3694527
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/986734
Influence of gut microbiota on subclinical inflammation and insulin resistance
Abstract
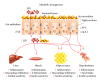
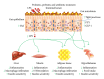
Obesity is the main condition that is correlated with the appearance of insulin resistance, which is the major link among its comorbidities, such as type 2 diabetes, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases, and several types of cancer. Obesity affects a large number of individuals worldwide; it degrades human health and quality of life. Here, we review the role of the gut microbiota in the pathophysiology of obesity and type 2 diabetes, which is promoted by a bacterial diversity shift mediated by overnutrition. Whole bacteria, their products, and metabolites undergo increased translocation through the gut epithelium to the circulation due to degraded tight junctions and the consequent increase in intestinal permeability that culminates in inflammation and insulin resistance. Several strategies focusing on modulation of the gut microbiota (antibiotics, probiotics, and prebiotics) are being experimentally employed in metabolic derangement in order to reduce intestinal permeability, increase the production of short chain fatty acids and anorectic gut hormones, and promote insulin sensitivity to counteract the inflammatory status and insulin resistance found in obese individuals.
Figures
References
-
- Kopelman PG. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature. 2000;404(6778):635–643. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira VA, Magalhães R. Obesidade no Brasil: tendências atuais. Revista Portuguesa De SaúDe Pública. 2006;24(2):71–91.
-
- WHO. Obesity and overweight. Fact sheet 311, 2013, http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

