Glycyrrhizic acid attenuates CCl₄-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in rats via a p53-mediated pathway
- PMID: 23840116
- PMCID: PMC3699029
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3781
Glycyrrhizic acid attenuates CCl₄-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in rats via a p53-mediated pathway
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of glycyrrhizic acid (GA) on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in rats via a p53-dependent mitochondrial pathway.
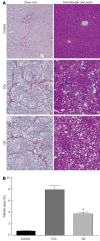
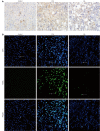
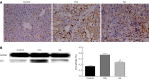
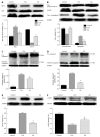
Methods: Forty-five male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly and equally divided into three groups, the control group, the CCl4 group, and the GA treatment group. To induce liver fibrosis in this model, rats were given a subcutaneous injection of a 40% solution of CCl4 in olive oil at a dose of 0.3 mL/100 g body weight biweekly for 8 wk, while controls received the same isovolumetric dose of olive oil by hypodermic injection, with an initial double-dose injection. In the GA group, rats were also treated with a 40% solution of CCl4 plus 0.2% GA solution in double distilled water by the intraperitoneal injection of 3 mL per rat three times a week from the first week following previously published methods, with modifications. Controls were given the same isovolumetric dose of double distilled water. Liver function parameters, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were determined. Pathologic changes in the liver were detected by hematoxylin and eosin staining. Collagen fibers were evaluated by Sirius red staining. Hepatocyte apoptosis was investigated using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine 5-triphosphate nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay and the cleaved caspase-3 immunohistochemistry assay. The expression levels of p53 and apoptosis-related proteins were evaluated by immunohistochemistry or Western blotting analysis.
Results: After 8 wk of treatment, GA significantly reduced serum activity of ALT (from 526.7 ± 57.2 to 342 ± 44.8, P < 0.05) and AST (from 640 ± 33.7 to 462.8 ± 30.6, P < 0.05), attenuated the changes in liver histopathology and reduced the staging score (from 3.53 ± 0.74 to 3.00 ± 0.76, P < 0.05) in CCl4-treated rats. GA markedly reduced the positive area of Sirius red and the ratio of the hepatic fibrotic region (from 7.87% ± 0.66% to 3.68% ± 0.32%, P < 0.05) compared with the CCl4 group. GA also decreased the expression level of cleaved caspase-3 compared to the CCl4 group. TUNEL assay indicated that GA significantly diminished the number of TUNEL-positive cells compared with the CCl4 group (P < 0.05). GA treatment clearly decreased the level of p53 (P < 0.05) detected by immunohistochemistry and Western blotting analysis. Compared with the CCl4 group, we also found that GA reduced the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio (P < 0.05), the expression of cleaved caspase-3 (P < 0.05), cleaved caspase-9 (P < 0.05), and inhibited cytochrome C and second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases (Smac) release from mitochondria to cytoplasm, i.e., GA reduced the expression level of Smac, which inhibited c-IAP1 activity (P < 0.05), ultimately inhibiting the activity of caspase-3, according to Western blotting analysis. As a result, GA suppressed activation of the caspase cascades and prevented hepatocyte apoptosis.
Conclusion: GA can inhibit CCl4-induced hepatocyte apoptosis via a p53-dependent mitochondrial pathway to retard the progress of liver fibrosis in rats.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Glycyrrhizic acid; Liver fibrosis; Mitochondria; P53.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycyrrhizic acid inhibits apoptosis and fibrosis in carbon-tetrachloride-induced rat liver injury.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 May 7;21(17):5271-80. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i17.5271. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25954100 Free PMC article.
-
[Protective effect of heme oxygenase-1 and its reaction product, carbon monoxide on acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006 Dec 18;38(6):618-22. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006. PMID: 17173083 Chinese.
-
Kadsura heteroclita stem ethanol extract protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 1;267:113496. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113496. Epub 2020 Oct 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33091494
-
Glycyrrhizic acid in the treatment of liver diseases: literature review.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:872139. doi: 10.1155/2014/872139. Epub 2014 May 13. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24963489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptosis in animal models of virus-induced disease.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009 Feb;7(2):144-55. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2071. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19148180 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hepato-protective effect of rutin via IL-6/STAT3 pathway in CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.Biol Res. 2015 Jun 11;48(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s40659-015-0022-y. Biol Res. 2015. PMID: 26062544 Free PMC article.
-
Glycyrrhetinic Acid-Induced MiR-663a Alleviates Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation by Attenuating the TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 May 11;2020:3156267. doi: 10.1155/2020/3156267. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32454854 Free PMC article.
-
Green tea extract attenuates CCl4-induced hepatic injury in male hamsters via inhibition of lipid peroxidation and p53-mediated apoptosis.Toxicol Rep. 2015 Aug 10;2:1149-1156. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2015.08.001. eCollection 2015. Toxicol Rep. 2015. PMID: 28962456 Free PMC article.
-
Protective mechanisms of medicinal plants targeting hepatic stellate cell activation and extracellular matrix deposition in liver fibrosis.Chin Med. 2014 Dec 24;9(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13020-014-0027-4. eCollection 2014. Chin Med. 2014. PMID: 25606051 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal ratio of 18α- and 18β-glycyrrhizic acid for preventing alcoholic hepatitis in rats.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Jul;18(1):172-178. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7572. Epub 2019 May 10. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31258651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Canbay A, Higuchi H, Bronk SF, Taniai M, Sebo TJ, Gores GJ. Fas enhances fibrogenesis in the bile duct ligated mouse: a link between apoptosis and fibrosis. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1323–1330. - PubMed
-
- Canbay A, Friedman S, Gores GJ. Apoptosis: the nexus of liver injury and fibrosis. Hepatology. 2004;39:273–278. - PubMed
-
- Inoue S, Browne G, Melino G, Cohen GM. Ordering of caspases in cells undergoing apoptosis by the intrinsic pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2009;16:1053–1061. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

