Active treatments are a rational approach for hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly patients
- PMID: 23840122
- PMCID: PMC3699049
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i24.3831
Active treatments are a rational approach for hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly patients
Abstract
Aim: To determine whether an active intervention is beneficial for the survival of elderly patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: The survival of 740 patients who received various treatments for HCC between 1983 and 2011 was compared among different age groups using Cox regression analysis. Therapeutic options were principally selected according to the clinical practice guidelines for HCC from the Japanese Society of Hepatology. The treatment most likely to achieve regional control capability was chosen, as far as possible, in the following order: resection, radiofrequency ablation, percutaneous ethanol injection, transcatheter arterial chemoembolization, transarterial oily chemoembolization, hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy, systemic chemotherapy including molecular targeting, or best supportive care. Each treatment was used alone, or in combination, with a clinical goal of striking the best balance between functional hepatic reserve and the volume of the targeted area, irrespective of their age. The percent survival to life expectancy was calculated based on a Japanese national population survey.
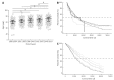
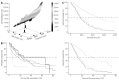
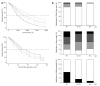
Results: The median ages of the subjects during each 5-year period from 1986 were 61, 64, 67, 68 and 71 years and increased significantly with time (P < 0.0001). The Child-Pugh score was comparable among younger (59 years of age or younger), middle-aged (60-79 years of age), and older (80 years of age or older) groups (P = 0.34), whereas the tumor-node-metastasis stage tended to be more advanced in the younger group (P = 0.060). Advanced disease was significantly more frequent in the younger group compared with the middle-aged group (P = 0.010), whereas there was no difference between the middle-aged and elderly groups (P = 0.75). The median survival times were 2593, 2011, 1643, 1278 and 1195 d for 49 years of age or younger, 50-59 years of age, 60-69 years of age, 70-79 years of age, or 80 years of age or older age groups, respectively, whereas the median percent survival to life expectancy were 13.9%, 21.9%, 24.7%, 25.7% and 37.6% for each group, respectively. The impact of age on actual survival time was significant (P = 0.020) with a hazard ratio of 1.021, suggesting that a 10-year-older patient has a 1.23-fold higher risk for death, and the overall survival was the worst in the oldest group. On the other hand, when the survival benefit was evaluated on the basis of percent survival to life expectancy, age was again found to be a significant explanatory factor (P = 0.022); however, the oldest group showed the best survival among the five different age groups. The youngest group revealed the worst outcomes in this analysis, and the hazard ratio of the oldest against the youngest was 0.35 for death. The survival trends did not differ substantially between the survival time and percent survival to life expectancy, when survival was compared overall or among various therapeutic interventions.
Conclusion: These results suggest that a therapeutic approach for HCC should not be restricted due to patient age.
Keywords: Active intervention; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Life expectancy; Population aging; Survival.
Figures
References
-
- Available from: http: //www.stat.go.jp/english/index.htm.
-
- Available from: http: //www.mhlw.go.jp/english/database/db-hw/index.html.
-
- Available from: http: //www.stat.go.jp/data/sekai/02.htm.
-
- Zhang Q, Zhang RY, Zhang JS, Hu J, Yang ZK, Zheng AF, Zhang X, Shen WF. Outcomes of primary percutaneous coronary intervention for acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction in patients aged over 75 years. Zhonghua Yixve Zazhi. 2006;119:1151–1156. - PubMed
-
- Teo KK, Sedlis SP, Boden WE, O’Rourke RA, Maron DJ, Hartigan PM, Dada M, Gupta V, Spertus JA, Kostuk WJ, et al. Optimal medical therapy with or without percutaneous coronary intervention in older patients with stable coronary disease: a pre-specified subset analysis of the COURAGE (Clinical Outcomes Utilizing Revascularization and Aggressive druG Evaluation) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:1303–1308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

