Clinical significance of melatonin concentrations in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis
- PMID: 23840154
- PMCID: PMC3703196
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.4066
Clinical significance of melatonin concentrations in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis
Abstract
Aim: To assess the value of plasma melatonin in predicting acute pancreatitis when combined with the acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II (APACHEII) and bedside index for severity in acute pancreatitis (BISAP) scoring systems.
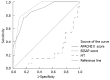
Methods: APACHEII and BISAP scores were calculated for 55 patients with acute physiology (AP) in the first 24 h of admission to the hospital. Additionally, morning (6:00 AM) serum melatonin concentrations were measured on the first day after admission. According to the diagnosis and treatment guidelines for acute pancreatitis in China, 42 patients suffered mild AP (MAP). The other 13 patients developed severe AP (SAP). A total of 45 healthy volunteers were used in this study as controls. The ability of melatonin and the APACHEII and BISAP scoring systems to predict SAP was evaluated using a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. The optimal melatonin cutoff concentration for SAP patients, based on the ROC curve, was used to classify the patients into either a high concentration group (34 cases) or a low concentration group (21 cases). Differences in the incidence of high scores, according to the APACHEII and BISAP scoring systems, were compared between the two groups.
Results: The MAP patients had increased melatonin levels compared to the SAP (38.34 ng/L vs 26.77 ng/L) (P = 0.021) and control patients (38.34 ng/L vs 30.73 ng/L) (P = 0.003). There was no significant difference inmelatoninconcentrations between the SAP group and the control group. The accuracy of determining SAP based on the melatonin level, the APACHEII score and the BISAP score was 0.758, 0.872, and 0.906, respectively, according to the ROC curve. A melatonin concentration ≤ 28.74 ng/L was associated with an increased risk of developing SAP. The incidence of high scores (≥ 3) using the BISAP system was significantly higher in patients with low melatonin concentration (≤ 28.74 ng/L) compared to patients with high melatonin concentration (> 28.74 ng/L) (42.9% vs 14.7%, P = 0.02). The incidence of high APACHEII scores (≥ 10) between the two groups was not significantly different.
Conclusion: The melatonin concentration is closely related to the severity of AP and the BISAP score. Therefore, we can evaluate the severity of disease by measuring the levels of serum melatonin.
Keywords: Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II; Bedside index for severity in acute pancreatitis; Cutoff; Melatonin concentrations; Pancreatitis; Predict.
Figures
References
-
- Whitcomb DC. Clinical practice. Acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2142–2150. - PubMed
-
- Ochoa JJ, Díaz-Castro J, Kajarabille N, García C, Guisado IM, De Teresa C, Guisado R. Melatonin supplementation ameliorates oxidative stress and inflammatory signaling induced by strenuous exercise in adult human males. J Pineal Res. 2011;51:373–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00899.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tan DX, Manchester LC, Terron MP, Flores LJ, Reiter RJ. One molecule, many derivatives: a never-ending interaction of melatonin with reactive oxygen and nitrogen species? J Pineal Res. 2007;42:28–42. - PubMed
-
- Miller E, Mrowicka M, Malinowska K, Kedziora J, Majsterek I. The effects of whole-body cryotherapy and melatonin supplementation on total antioxidative status and some antioxidative enzymes in multiple sclerosis patients. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2011;31:150–153. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

