Structure and dynamics of the gp120 V3 loop that confers noncompetitive resistance in R5 HIV-1(JR-FL) to maraviroc
- PMID: 23840315
- PMCID: PMC3695986
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065115
Structure and dynamics of the gp120 V3 loop that confers noncompetitive resistance in R5 HIV-1(JR-FL) to maraviroc
Abstract
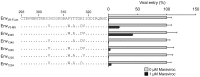
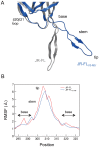
Maraviroc, an (HIV-1) entry inhibitor, binds to CCR5 and efficiently prevents R5 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) from using CCR5 as a coreceptor for entry into CD4(+) cells. However, HIV-1 can elude maraviroc by using the drug-bound form of CCR5 as a coreceptor. This property is known as noncompetitive resistance. HIV-1(V3-M5) derived from HIV-1(JR-FLan) is a noncompetitive-resistant virus that contains five mutations (I304V/F312W/T314A/E317D/I318V) in the gp120 V3 loop alone. To obtain genetic and structural insights into maraviroc resistance in HIV-1, we performed here mutagenesis and computer-assisted structural study. A series of site-directed mutagenesis experiments demonstrated that combinations of V3 mutations are required for HIV-1(JR-FLan) to replicate in the presence of 1 µM maraviroc, and that a T199K mutation in the C2 region increases viral fitness in combination with V3 mutations. Molecular dynamic (MD) simulations of the gp120 outer domain V3 loop with or without the five mutations showed that the V3 mutations induced (i) changes in V3 configuration on the gp120 outer domain, (ii) reduction of an anti-parallel β-sheet in the V3 stem region, (iii) reduction in fluctuations of the V3 tip and stem regions, and (iv) a shift of the fluctuation site at the V3 base region. These results suggest that the HIV-1 gp120 V3 mutations that confer maraviroc resistance alter structure and dynamics of the V3 loop on the gp120 outer domain, and enable interactions between gp120 and the drug-bound form of CCR5.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
A combination of polymorphic mutations in V3 loop of HIV-1 gp120 can confer noncompetitive resistance to maraviroc.Virology. 2011 May 10;413(2):293-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.02.019. Epub 2011 Mar 26. Virology. 2011. PMID: 21440278
-
Characterizing the Diverse Mutational Pathways Associated with R5-Tropic Maraviroc Resistance: HIV-1 That Uses the Drug-Bound CCR5 Coreceptor.J Virol. 2015 Nov;89(22):11457-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01384-15. Epub 2015 Sep 2. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26339063 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced maximal inhibition in phenotypic susceptibility assays indicates that viral strains resistant to the CCR5 antagonist maraviroc utilize inhibitor-bound receptor for entry.J Virol. 2007 Mar;81(5):2359-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02006-06. Epub 2006 Dec 20. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17182681 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanisms of resistance and failure of treatment with maraviroc].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2008 Oct;26 Suppl 11:28-33. doi: 10.1016/s0213-005x(08)76561-3. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2008. PMID: 19133219 Review. Spanish.
-
A pièce de resistance: how HIV-1 escapes small molecule CCR5 inhibitors.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2009 Mar;4(2):118-24. doi: 10.1097/COH.0b013e3283223d46. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2009. PMID: 19339950 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced antibody-mediated neutralization of HIV-1 variants that are resistant to fusion inhibitors.Retrovirology. 2016 Sep 27;13(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12977-016-0304-7. Retrovirology. 2016. PMID: 27670680 Free PMC article.
-
In silico Analysis of HIV-1 Env-gp120 Reveals Structural Bases for Viral Adaptation in Growth-Restrictive Cells.Front Microbiol. 2016 Feb 9;7:110. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00110. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26903989 Free PMC article.
-
IDEPI: rapid prediction of HIV-1 antibody epitopes and other phenotypic features from sequence data using a flexible machine learning platform.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Sep 25;10(9):e1003842. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003842. eCollection 2014 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 25254639 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-acting stapled peptides target both HIV-1 entry and assembly.Retrovirology. 2013 Nov 15;10:136. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-136. Retrovirology. 2013. PMID: 24237936 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Treatment-Associated Mutations on HIV Replication and Transmission Cycles.Viruses. 2022 Dec 30;15(1):107. doi: 10.3390/v15010107. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36680147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fadel H, Temesgen Z (2007) Maraviroc. Drugs Today (Barc) 43: 749–758. - PubMed
-
- Tilton JC, Doms RW (2010) Entry inhibitors in the treatment of HIV-1 infection. Antiviral Res 85: 91–100. - PubMed
-
- Gorry PR, Ancuta P (2011) Coreceptors and HIV-1 pathogenesis. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep 8: 45–53. - PubMed
-
- Gulick RM, Su Z, Flexner C, Hughes MD, Skolnik PR, et al. (2007) Phase 2 study of the safety and efficacy of vicriviroc, a CCR5 inhibitor, in HIV-1-Infected, treatment-experienced patients: AIDS clinical trials group 5211. J Infect Dis 196: 304–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

