Recombinant human adenovirus-p53 injection induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines mediated by p53-Fbxw7 pathway, which controls c-Myc and cyclin E
- PMID: 23840897
- PMCID: PMC3698167
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068574
Recombinant human adenovirus-p53 injection induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines mediated by p53-Fbxw7 pathway, which controls c-Myc and cyclin E
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Recombinant Human Adenovirus-p53 Injection Induced Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Lines Mediated by p53-Fbxw7 Pathway, Which Controls c-Myc and Cyclin E.PLoS One. 2020 Mar 27;15(3):e0231287. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231287. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32218606 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
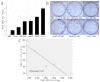
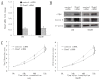
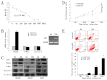
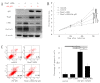
F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7 (Fbxw7/hAgo/hCdc4/Fbw7) is a p53-dependent tumor suppressor and leads to ubiquitination-mediated suppression of several oncoproteins including c-Myc, cyclin E, Notch, c-Jun and others. Our previous study has indicated that low expression of Fbxw7 was negatively correlated with c-Myc, cyclin E and mutant-p53 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues. But the role and mechanisms of Fbxw7 in HCC are still unknown. Here, we investigated the function of Fbxw7 in HCC cell lines and the anti-tumor activity of recombinant human adenovirus-p53 injection (rAd-p53, Gendicine) administration in vitro and in vivo. Fbxw7-specific siRNA enhanced expression of c-Myc and cyclin E proteins and increased proliferation in cell culture. rAd-p53 inhibited tumor cell growth with Fbxw7 upregulation and c-Myc and cyclin E downregulation in vitro and a murine HCC model. This effect could be partially reverted using Fbxw7-specific siRNA. Here, we suggest that the activation of Fbxw7 by adenoviral delivery of p53 leads to increased proteasomal degradation of c-Myc and cyclin E enabling growth arrest and apoptosis. Addressing this pathway, we identified that rAd-p53 could be a potential therapeutic agent for HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
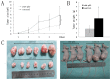
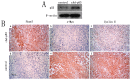
References
-
- Forner Alejandro, Llovet Josep M, Bruix Jordi (2012) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 379: 1245-1255. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61347-0. PubMed: 22353262. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wertz IE, Kusam S, Lam C, Okamoto T, Sandoval W et al. (2011) Sensitivity to antitubulin chemotherapeutics is regulated by MCL1 and FBW7. Nature 471: 110-114. doi:10.1038/nature09779. PubMed: 21368834. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Crusio KM, King B, Reavie LB, Aifantis I (2010) The ubiquitous nature of cancer: the role of the SCF (Fbw7) complex in development and transformation. Oncogene 29: 4865-4873. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.222. PubMed: 20543859. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Fukushima H, Gao D, Inuzuka H, Wan L et al. (2011) The two faces of FBW7 in cancer drug Resistance. Bioessays 33: 851-859. doi:10.1002/bies.201100101. PubMed: 22006825. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tu K, Zheng X, Yin G, Zan X, Yao Y et al. (2012) Evaluation of Fbxw7 expression and its correlation with expression of SREBP-1 in a mouse model of NAFLD. Mol Med Report 6: 525-530 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

