DdrA, DdrD, and PprA: components of UV and mitomycin C resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans R1
- PMID: 23840905
- PMCID: PMC3698191
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069007
DdrA, DdrD, and PprA: components of UV and mitomycin C resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans R1
Abstract
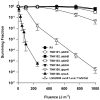
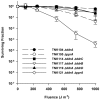
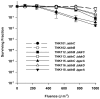
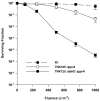
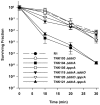
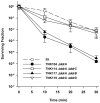
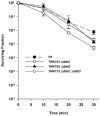
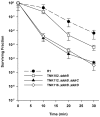
Mutants created by deleting the ddrA, ddrB, ddrC, ddrD, and pprA loci of Deinococcus radiodurans R1alone and in all possible combinations of pairs revealed that the encoded gene products contribute to this species' resistance to UV light and/or mitomycin C. Deleting pprA from an otherwise wild type cell sensitizes the resulting strain to UV irradiation, reducing viability by as much as eight fold relative to R1. If this deletion is introduced into a ΔddrA or ΔddrD background, the resulting strains become profoundly sensitive to the lethal effects of UV light. At a fluence of 1000 Jm⁻², the ΔddrA ΔpprA and ΔddrD ΔpprA strains are 100- and 1000-fold more sensitive to UV relative to the strain that has only lost pprA. Deletion of ddrA results in a 100 fold increase in strain sensitivity to mitomycin C, but in backgrounds that combine a deletion of ddrA with deletions of either ddrC or ddrD, mitomycin resistance is restored to wild type levels. Inactivation of ddrB also increases D. radiodurans sensitivity to mitomycin, but unlike the ddrA mutant deleting ddrC or ddrD from a ΔddrB background further increases that sensitivity. Despite the effect that loss of these gene products has on DNA damage resistance, none appear to directly affect either excision repair or homologous recombination suggesting that they participate in novel processes that facilitate tolerance to UV light and interstrand crosslinks in this species.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Site-Directed A184S Mutation in the HTH Domain of the Global Regulator IrrE Enhances Deinococcus radiodurans R1 Tolerance to UV Radiation and MMC Shock.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Dec 28;25(12):2125-34. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1507.07008. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26370803
-
Analysis of Deinococcus radiodurans's transcriptional response to ionizing radiation and desiccation reveals novel proteins that contribute to extreme radioresistance.Genetics. 2004 Sep;168(1):21-33. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.029249. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15454524 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of PprA, IrrE, and RecA in the resistance of Deinococcus radiodurans to germicidal and environmentally relevant UV radiation.Arch Microbiol. 2009 Dec;191(12):913-8. doi: 10.1007/s00203-009-0522-7. Epub 2009 Oct 31. Arch Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19882142
-
Deinococcus radiodurans: what belongs to the survival kit?Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2008 May-Jun;43(3):221-38. doi: 10.1080/10409230802122274. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18568848 Review.
-
Oxidative stress resistance in Deinococcus radiodurans.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011 Mar;75(1):133-91. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00015-10. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21372322 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spirosoma montaniterrae sp. nov., an ultraviolet and gamma radiation-resistant bacterium isolated from mountain soil.J Microbiol. 2015 Jul;53(7):429-34. doi: 10.1007/s12275-015-5008-5. Epub 2015 Jun 27. J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26115990
-
Conservation and diversity of radiation and oxidative stress resistance mechanisms in Deinococcus species.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2019 Jan 1;43(1):19-52. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuy037. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30339218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spirosoma pulveris sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from a dust sample collected at Chungnam province, South Korea.J Microbiol. 2015 Nov;53(11):750-5. doi: 10.1007/s12275-015-5263-5. Epub 2015 Oct 28. J Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26502958
-
Conservation and diversity of the IrrE/DdrO-controlled radiation response in radiation-resistant Deinococcus bacteria.Microbiologyopen. 2017 Aug;6(4):e00477. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.477. Epub 2017 Apr 11. Microbiologyopen. 2017. PMID: 28397370 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into Radio-Resistance Mechanism Revealed by (Phospho)Proteome Analysis of Deinococcus Radiodurans after Heavy Ion Irradiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 1;24(19):14817. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914817. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Battista JR, Rainey FA (2001) Phylum BIV. "Deinococcus-Thermus" Family 1. Deinococcaceae Brooks and Murray 1981, 356,vp emend. Rainey, Nobre, Schumann, Stackebrandt and da Costa 1997, 513. In: Boone DR, Castenholz RW. Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. 2nd ed. New York: Springer Verlag; pp. 395-414.
-
- Cox MM, Battista JR (2005) Deinococcus radiodurans - the consummate survivor. Nat Rev Microbiol 3: 882-892. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1264. PubMed: 16261171. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moseley BEB (1983) Photobiology and radiobiology of Micrococcus (Deinococcus) radiodurans . Photochem Photobiol Rev 7: 223-275.
-
- Sweet DM, Moseley BE (1974) Accurate repair of ultraviolet-induced damage in Micrococcus radiodurans . Mutat Res 23: 311-318. doi:10.1016/0027-5107(74)90104-3. PubMed: 4407662. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

