Dose-dependent adverse effects of salinomycin on male reproductive organs and fertility in mice
- PMID: 23840907
- PMCID: PMC3698082
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069086
Dose-dependent adverse effects of salinomycin on male reproductive organs and fertility in mice
Erratum in
-
Correction: Dose-dependent adverse effects of salinomycin on male reproductive organs and fertility in mice.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 19;14(12):e0226872. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226872. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31856246 Free PMC article.
Abstract
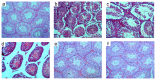
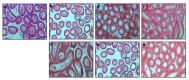
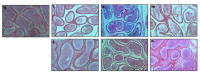
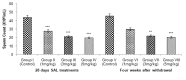
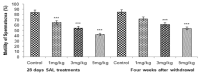
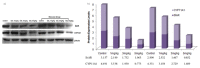
Salinomycin is used as an antibiotic in animal husbandry. Its implication in cancer therapy has recently been proposed. Present study evaluated the toxic effects of Salinomycin on male reproductive system of mice. Doses of 1, 3 or 5 mg/kg of Salinomycin were administered daily for 28 days. Half of the mice were sacrificed after 24 h of the last treatment and other half were sacrificed 28 days after withdrawal of treatment. Effects of SAL on body and reproductive organ weights were studied. Histoarchitecture of testis and epididymis was evaluated along with ultrastructural changes in Leydig cells. Serum and testicular testosterone and luteinizing hormones were estimated. Superoxide dismutase, reduced glutathione, lipid peroxidation, catalase and lactate dehydrogenase activities were measured. Spermatozoa count, morphology, motility and fertility were evaluated. Expression patterns of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) and cytochrome P450 side chain cleavage proteins (CYP11A1) were assessed by Western blotting. Salinomycin treatment was lethal to few mice and retarded body growth in others with decreased weight of testes and seminal vesicles in a dose dependent manner. Seminiferous tubules in testes were disrupted and the epithelium of epididymis showed frequent occurrence of vacuolization and necrosis. Leydig cells showed hypertrophied cytoplasm with shrunken nuclei, condensed mitochondria, proliferated endoplasmic reticulum and increased number of lipid droplets. Salinomycin decreased motility and spermatozoa count with increased number of abnormal spermatozoa leading to infertility. The testosterone and luteinizing hormone levels were decreased in testis but increased in serum at higher doses. Depletion of superoxide dismutase and reduced glutathione with increased lipid peroxidation in both testis and epididymis indicated generation of oxidative stress. Suppressed expression of StAR and CYP11A1 proteins indicates inhibition of steroidogenesis. Spermatogenesis was however observed in testis 28 days after Salinomycin withdrawal. The results indicate reversible dose-dependent adverse effects of Salinomycin on male reproductive system of mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
An aminoglycoside antibiotic gentamycin induces oxidative stress, reduces antioxidant reserve and impairs spermatogenesis in rats.J Toxicol Sci. 2008 Feb;33(1):85-96. doi: 10.2131/jts.33.85. J Toxicol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18303187
-
Neonatal estrogen exposure of male rats alters reproductive functions at adulthood.Biol Reprod. 2003 Jun;68(6):2081-91. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.102.010637. Epub 2003 Jan 8. Biol Reprod. 2003. PMID: 12606459
-
Dacarbazine induces genotoxic and cytotoxic germ cell damage with concomitant decrease in testosterone and increase in lactate dehydrogenase concentration in the testis.Mutat Res. 2006 Sep 5;607(2):240-52. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2006.04.019. Epub 2006 Jun 21. Mutat Res. 2006. PMID: 16793327
-
Mechanisms of doxorubicin-mediated reproductive toxicity - A review.Reprod Toxicol. 2021 Jun;102:80-89. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2021.04.003. Epub 2021 Apr 18. Reprod Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33878324 Review.
-
Disruptive consequences of monosodium glutamate on male reproductive function: A review.Curr Res Toxicol. 2024 Jan 9;6:100148. doi: 10.1016/j.crtox.2024.100148. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38287921 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of ARK5 in cancer and other diseases (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2021 Jul;22(1):697. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10129. Epub 2021 May 2. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33986861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interpreting histopathology in the epididymis.Spermatogenesis. 2015 Jan 8;4(2):e979114. doi: 10.4161/21565562.2014.979114. eCollection 2014 May-Aug. Spermatogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26413396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salinomycin exerts anti-angiogenic and anti-tumorigenic activities by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated angiogenesis.Oncotarget. 2016 May 3;7(18):26580-92. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8555. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27058891 Free PMC article.
-
Salinomycin as a potent anticancer stem cell agent: State of the art and future directions.Med Res Rev. 2022 May;42(3):1037-1063. doi: 10.1002/med.21870. Epub 2021 Nov 16. Med Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 34786735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p53 and Cell Fate: Sensitizing Head and Neck Cancer Stem Cells to Chemotherapy.Crit Rev Oncog. 2018;23(3-4):173-187. doi: 10.1615/CritRevOncog.2018027353. Crit Rev Oncog. 2018. PMID: 30311573 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K, Kuperwasser C et al. (2009) Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell 138: 645-659. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.034. PubMed: 19682730. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kinashi H, Otake H, Yonehara H, Soto S, Saito Y (1973) The structure of Salinomycin, a new member of the polyether antibiotics. Tetra Lett 4955-4958.
-
- Mitani M, Yamanishi T, Miyazaki Y (1975) Salinomycin: a new monovalent cation ionophore. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 66: 1231-1236. - PubMed
-
- Huczyński A (2012) Polyether ionophores-promising bioactive molecules for cancer therapy. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22(23): 7002-7010. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.09.046. PubMed: 23063400. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Naujokat C, Steinhart R (2012) Salinomycin as a Drug for Targeting Human Cancer Stem Cells. J Biomed Biotechnol. doi:10.1155/2012/950658. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

