Polyphenols: multipotent therapeutic agents in neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 23840922
- PMCID: PMC3690243
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/891748
Polyphenols: multipotent therapeutic agents in neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
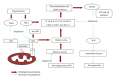
Aging leads to numerous transitions in brain physiology including synaptic dysfunction and disturbances in cognition and memory. With a few clinically relevant drugs, a substantial portion of aging population at risk for age-related neurodegenerative disorders require nutritional intervention. Dietary intake of polyphenols is known to attenuate oxidative stress and reduce the risk for related neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), stroke, multiple sclerosis (MS), Parkinson's disease (PD), and Huntington's disease (HD). Polyphenols exhibit strong potential to address the etiology of neurological disorders as they attenuate their complex physiology by modulating several therapeutic targets at once. Firstly, we review the advances in the therapeutic role of polyphenols in cell and animal models of AD, PD, MS, and HD and activation of drug targets for controlling pathological manifestations. Secondly, we present principle pathways in which polyphenol intake translates into therapeutic outcomes. In particular, signaling pathways like PPAR, Nrf2, STAT, HIF, and MAPK along with modulation of immune response by polyphenols are discussed. Although current polyphenol researches have limited impact on clinical practice, they have strong evidence and testable hypothesis to contribute clinical advances and drug discovery towards age-related neurological disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Hung CW, Chen YC, Hsieh WL, Chiou SH, Kao CL. Ageing and neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Research Reviews. 2010;9(1):S36–S46. - PubMed
-
- Ross CA, Tabizi SJ. Huntington’s disease: from molecular pathogenesis to clinical treatment. Lancelet Neurology. 2011;10(1):83–98. - PubMed
-
- Olesen J, Gustavsson A, Svensson M, Wittchen HU, Jonsson B. The economic cost of brain disorders in Europe. European Journal of Neurology. 2012;19(1):155–162. - PubMed
-
- Albarracin SL, Stab B, Casas Z, et al. Effects of natural antioxidants in neurodegenerative diseases. Nutritional Neuroscience. 2012;15(1):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Lundkvist J, Näslund J. γ-secretase: a complex target for Alzheimer's disease. Current Opinion in Pharmacology. 2007;7(1):112–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical