Autophagy in breast cancer and its implications for therapy
- PMID: 23841025
- PMCID: PMC3696532
Autophagy in breast cancer and its implications for therapy
Abstract
Autophagy is an evolutionarily conserved process of cellular self-digestion that serves as a mechanism to clear damaged organelles and recycle nutrients. Since autophagy can promote cell survival as well as cell death, it has been linked to different human pathologies, including cancer. Although mono-allelic deletion of autophagy-related gene BECN1 in breast tumors originally indicated a tumor suppressive role for autophagy in breast cancer, the intense research during the last decade suggests a role for autophagy in tumor progression. It is now recognized that tumor cells often utilize autophagy to survive various stresses, such as oncogene-induced transformation, hypoxia, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and extracellular matrix detachment. Induction of autophagy by tumor cells may also contribute to tumor dormancy and resistance to anticancer therapies, thus making autophagy inhibitors promising drug candidates for breast cancer treatment. The scientific endeavors continue to define a precise role for autophagy in breast cancer. In this article, we review the current literature on the role of autophagy during the development and progression of breast cancer, and discuss the potential of autophagy modulators for breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: Autophagy; ER stress; apoptosis; breast cancer; cancer therapy; hypoxia; metabolism; metastasis; transformation; tumor microenvironment.
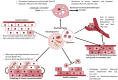
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Klionsky DJ. Autophagy: from phenomenology to molecular understanding in less than a decade. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:931–937. - PubMed
-
- Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y. The role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:107–132. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
