The effect of diabetes-associated autoantigens on cell processes in human PBMCs and their relevance to autoimmune diabetes development
- PMID: 23841104
- PMCID: PMC3694381
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/589451
The effect of diabetes-associated autoantigens on cell processes in human PBMCs and their relevance to autoimmune diabetes development
Abstract
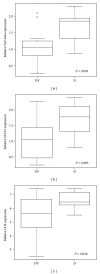
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) is considered to be a T-helper- (Th-) 1 autoimmune disease; however, T1D pathogenesis likely involves many factors, and sufficient tools for autoreactive T cell detection for the study of this disease are currently lacking. In this study, using gene expression microarrays, we analysed the effect of diabetes-associated autoantigens on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with the purpose of identifying (pre)diabetes-associated cell processes. Twelve patients with recent onset T1D, 18 first-degree relatives of the TD1 patients (DRL; 9/18 autoantibody positive), and 13 healthy controls (DV) were tested. PBMCs from these individuals were stimulated with a cocktail of diabetes-associated autoantigens (proinsulin, IA-2, and GAD65-derived peptides). After 72 hours, gene expression was evaluated by high-density gene microarray. The greatest number of functional differences was observed between relatives and controls (69 pathways), from which 15% of the pathways belonged to "immune response-related" processes. In the T1D versus controls comparison, more pathways (24%) were classified as "immune response-related." Important pathways that were identified using data from the T1D versus controls comparison were pathways involving antigen presentation by MHCII, the activation of Th17 and Th22 responses, and cytoskeleton rearrangement-related processes. Genes involved in Th17 and TGF-beta cascades may represent novel, promising (pre)diabetes biomarkers.
Figures
References
-
- Castano L, Eisenbarth GS. Type-I diabetes: a chronic autoimmune disease of human, mouse, and rat. Annual Review of Immunology. 1990;8:647–679. - PubMed
-
- Foulis AK, Farquharson MA, Meager A. Immunoreactive α-interferon in insulin-secreting β cells in type 1 diabetes mellitus. The Lancet. 1987;2(8573):1423–1427. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson MA, Kaufman DL, Campbell L, et al. Response of peripheral-blood mononuclear cells to glutamate decarboxylase in insulin-dependent diabetes. The Lancet. 1992;339(8791):458–459. - PubMed
-
- Ludvigsson J, Faresjö M, Hjorth M, et al. GAD treatment and insulin secretion in recent-onset type 1 diabetes. New England Journal of Medicine. 2008;359(18):1909–1920. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

