Signal transduction inhibitors in treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes
- PMID: 23841999
- PMCID: PMC3716523
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8722-6-50
Signal transduction inhibitors in treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes
Abstract
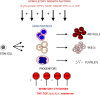
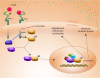
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a group of hematologic disorders characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis that results in reduced blood counts. Although MDS can transform into leukemia, most of the morbidity experienced by these patients is due to chronically low blood counts. Conventional cytotoxic agents used to treat MDS have yielded some encouraging results but are characterized by many adverse effects in the predominantly elderly patient population. Targeted interventions aimed at reversing the bone marrow failure and increasing the peripheral blood counts would be advantageous in this cohort of patients. Studies have demonstrated over-activated signaling of myelo-suppressive cytokines such as TGF-β, TNF-α and Interferons in MDS hematopoietic stem cells. Targeting these signaling cascades could be potentially therapeutic in MDS. The p38 MAP kinase pathway, which is constitutively activated in MDS, is an example of cytokine stimulated kinase that promotes aberrant apoptosis of stem and progenitor cells in MDS. ARRY-614 and SCIO-469 are p38 MAPK inhibitors that have been used in clinical trials and have shown activity in a subset of MDS patients. TGF-β signaling has been therapeutically targeted by small molecule inhibitor of the TGF-β receptor kinase, LY-2157299, with encouraging preclinical results. Apart from TGF-β receptor kinase inhibition, members of TGF-β super family and BMP ligands have also been targeted by ligand trap compounds like Sotatercept (ACE-011) and ACE-536. The multikinase inhibitor, ON-01910.Na (Rigosertib) has demonstrated early signs of efficacy in reducing the percentage of leukemic blasts and is in advanced stages of clinical testing. Temsirolimus, Deforolimus and other mTOR inhibitors are being tested in clinical trials and have shown preclinical efficacy in CMML. EGF receptor inhibitors, Erlotinib and Gefitinib have shown efficacy in small trials that may be related to off target effects. Cell cycle regulator inhibitors such as Farnesyl transferase inhibitors (Tipifarnib, Lonafarnib) and MEK inhibitor (GSK1120212) have shown acceptable toxicity profiles in small studies and efforts are underway to select mutational subgroups of MDS and AML that may benefit from these inhibitors. Altogether, these studies show that targeting various signal transduction pathways that regulate hematopoiesis offers promising therapeutic potential in this disease. Future studies in combination with high resolution correlative studies will clarify the subgroup specific efficacies of these agents.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reduced SMAD7 leads to overactivation of TGF-beta signaling in MDS that can be reversed by a specific inhibitor of TGF-beta receptor I kinase.Cancer Res. 2011 Feb 1;71(3):955-63. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2933. Epub 2010 Dec 28. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21189329 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical activity and safety of the dual pathway inhibitor rigosertib for higher risk myelodysplastic syndromes following DNA methyltransferase inhibitor therapy.Hematol Oncol. 2015 Jun;33(2):57-66. doi: 10.1002/hon.2137. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Hematol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 24777753
-
Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β pathway as a therapeutic target in lower risk myelodysplastic syndromes.Leukemia. 2019 Jun;33(6):1303-1312. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0448-2. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Leukemia. 2019. PMID: 30962581 Review.
-
Rigosertib as a selective anti-tumor agent can ameliorate multiple dysregulated signaling transduction pathways in high-grade myelodysplastic syndrome.Sci Rep. 2014 Dec 4;4:7310. doi: 10.1038/srep07310. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25472472 Free PMC article.
-
p38 MAP kinase regulates stem cell apoptosis in human hematopoietic failure.Cell Cycle. 2007 Mar 1;6(5):534-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.5.3921. Epub 2007 Mar 25. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17351344 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Fibrosis: From Molecular Mechanisms to Advanced Therapies.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jan;12(3):e2410416. doi: 10.1002/advs.202410416. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39665319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of the polo-like kinase inhibitor rigosertib, alone or in combination with Abelson tyrosine kinase inhibitors, against break point cluster region-c-Abelson-positive leukemia cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 21;6(24):20231-40. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4047. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26008977 Free PMC article.
-
The MAPK ERK5, but not ERK1/2, inhibits the progression of monocytic phenotype to the functioning macrophage.Exp Cell Res. 2015 Jan 1;330(1):199-211. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.10.003. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Exp Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 25447310 Free PMC article.
-
8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine as a biomarker of oxidative DNA damage in workers exposed to low-dose benzene.Toxicol Rep. 2017 May 31;4:291-295. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2017.05.008. eCollection 2017. Toxicol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28959652 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of TGFβ1 and TGFβ3 promotes hematopoiesis in Fanconi anemia.Exp Hematol. 2021 Jan;93:70-84.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2020.11.002. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Exp Hematol. 2021. PMID: 33166613 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greenberg PL, Tuechler H, Schanz J, Sanz G, Garcia-Manero G, Sole F, Bennett JM, Bowen D, Fenaux P, Dreyfus F, Kantarjian H, Kuendgen A, Levis A, Malcovati L, Cazzola M, Cermak J, Fonatsch C, Le Beau MM, Slovak ML, Krieger O, Luebbert M, Maciejewski J, Magalhaes SM, Miyazaki Y, Pfeilstocker M, Sekeres M, Sperr WR, Stauder R, Tauro S, Valent P, Revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R) for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 2012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou L, Nguyen AN, Sohal D, Ying Ma J, Pahanish P, Gundabolu K, Hayman J, Chubak A, Mo Y, Bhagat TD, Das B, Kapoun AM, Navas TA, Parmar S, Kambhampati S, Pellagatti A, Braunchweig I, Zhang Y, Wickrema A, Medicherla S, Boultwood J, Platanias LC, Higgins LS, List AF, Bitzer M, Verma A. Inhibition of the TGF-beta receptor I kinase promotes hematopoiesis in MDS. Blood. 2008;112:3434–3443. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-139824. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

