The impact of mathematical modeling on the understanding of diabetes and related complications
- PMID: 23842097
- PMCID: PMC3731829
- DOI: 10.1038/psp.2013.30
The impact of mathematical modeling on the understanding of diabetes and related complications
Abstract
Diabetes is a chronic and complex multifactorial disease caused by persistent hyperglycemia and for which underlying pathogenesis is still not completely understood. The mathematical modeling of glucose homeostasis, diabetic condition, and its associated complications is rapidly growing and provides new insights into the underlying mechanisms involved. Here, we discuss contributions to the diabetes modeling field over the past five decades, highlighting the areas where more focused research is required.CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology (2013) 2, e54; doi:10.1038/psp.2013.30; advance online publication 10 July 2013.
Figures
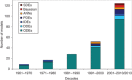


Similar articles
-
CPT: Pharmacometrics and Systems Pharmacology.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2012 Sep 26;1(9):e8. doi: 10.1038/psp.2012.8. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23835888 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular disease: the other face of diabetes.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 23;2(10):e81. doi: 10.1038/psp.2013.57. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24153424 Free PMC article.
-
Basic concepts in population modeling, simulation, and model-based drug development.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2012 Sep 26;1(9):e6. doi: 10.1038/psp.2012.4. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23835886 Free PMC article.
-
Mathematical Modeling for the Physiological and Clinical Investigation of Glucose Homeostasis and Diabetes.Front Physiol. 2020 Nov 25;11:575789. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.575789. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33324238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacometrics: The Already-Present Future of Precision Pharmacology.Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2023 Jan;57(1):57-69. doi: 10.1007/s43441-022-00439-4. Epub 2022 Aug 18. Ther Innov Regul Sci. 2023. PMID: 35984633 Review.
Cited by
-
A mechanistic modeling platform of SGLT2 inhibition: Implications for type 1 diabetes.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2023 Jun;12(6):831-841. doi: 10.1002/psp4.12956. Epub 2023 Mar 16. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36912425 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of quantitative and systems pharmacology in large pharma.CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2014 Oct 22;3(10):e142. doi: 10.1038/psp.2014.40. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25338195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive compartmental model of blood glucose regulation for healthy and type 2 diabetic subjects.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2016 Sep;54(9):1383-98. doi: 10.1007/s11517-015-1406-4. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2016. PMID: 26493377
-
Glucose Homeostatic Law: Insulin Clearance Predicts the Progression of Glucose Intolerance in Humans.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 1;10(12):e0143880. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143880. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26623647 Free PMC article.
-
A Simple Mathematical Model for Wound Closure Evaluation.J Am Coll Clin Wound Spec. 2016 Jul 29;7(1-3):40-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jccw.2016.07.002. eCollection 2015 Dec. J Am Coll Clin Wound Spec. 2016. PMID: 28053868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolie V.W. Coefficients of normal blood glucose regulation. J. Appl. Physiol. 1961;16:783–788. - PubMed
-
- Bergman R.N., Ider Y.Z., Bowden C.R., Cobelli C. Quantitative estimation of insulin sensitivity. Am. J. Physiol. 1979;236:E667–E677. - PubMed
-
- Bergman R.N., et al. Assessment of insulin sensitivity in vivo: a critical review. Diabetes. Metab. Rev. 1989;5:411–429. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

