Tumor histology predicts patterns of failure and survival in patients with brain metastases from lung cancer treated with gamma knife radiosurgery
- PMID: 23842552
- PMCID: PMC3880778
- DOI: 10.1227/NEU.0000000000000072
Tumor histology predicts patterns of failure and survival in patients with brain metastases from lung cancer treated with gamma knife radiosurgery
Abstract
Background: We review our experience with lung cancer patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases treated with Gamma Knife radiosurgery (GKRS).
Objective: To determine whether tumor histology predicts patient outcomes.
Methods: Between July 1, 2000, and December 31, 2010, 271 patients with brain metastases from primary lung cancer were treated with GKRS at our institution. Included in our study were 44 squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), 31 small cell carcinoma (SCLC), and 138 adenocarcinoma (ACA) patients; 47 patients with insufficient pathology to determine subtype were excluded. No non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients received whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT) before their GKRS, and SCLC patients were allowed to have prophylactic cranial irradiation, but no previously known brain metastases. A median of 2 lesions were treated per patient with median marginal dose of 20 Gy.
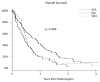
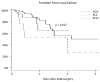
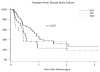
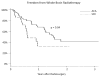
Results: Median survival was 10.2 months for ACA, 5.9 months for SCLC, and 5.3 months for SCC patients (P = .008). The 1-year local control rates were 86%, 86%, and 54% for ACA, SCC, and SCLC, respectively (P = .027). The 1-year distant failure rates were 35%, 63%, and 65% for ACA, SCC, and SCLC, respectively (P = .057). The likelihood of dying of neurological death was 29%, 36%, and 55% for ACA, SCC, and SCLC, respectively (P = .027). The median time to WBRT was 11 months for SCC and 24 months for ACA patients (P = .04). Multivariate analysis confirmed SCLC histology as a significant predictor of worsened local control (hazard ratio [HR]: 6.46, P = .025) and distant failure (HR: 3.32, P = .0027). For NSCLC histologies, SCC predicted for earlier time to salvage WBRT (HR: 2.552, P = .01) and worsened overall survival (HR: 1.77, P < .0121).
Conclusion: Histological subtype of lung cancer appears to predict outcomes. Future trials and prognostic indices should take these histology-specific patterns into account.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no personal financial or institutional interest in any of the drugs, materials, or devices described in this article.
Figures
References
-
- Chao ST, Barnett GH, Liu SW, et al. Five-year survivors of brain metastases: a single-institution report of 32 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;66(3):801–809. - PubMed
-
- Nieder C, Leicht A, Motaref B, et al. Late radiation toxicity after whole brain radiotherapy: the influence of antiepileptic drugs. Am J Clin Oncol. 1999;22(6):573–579. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;295(21):2483–2491. - PubMed
-
- Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(11):1037–1044. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

